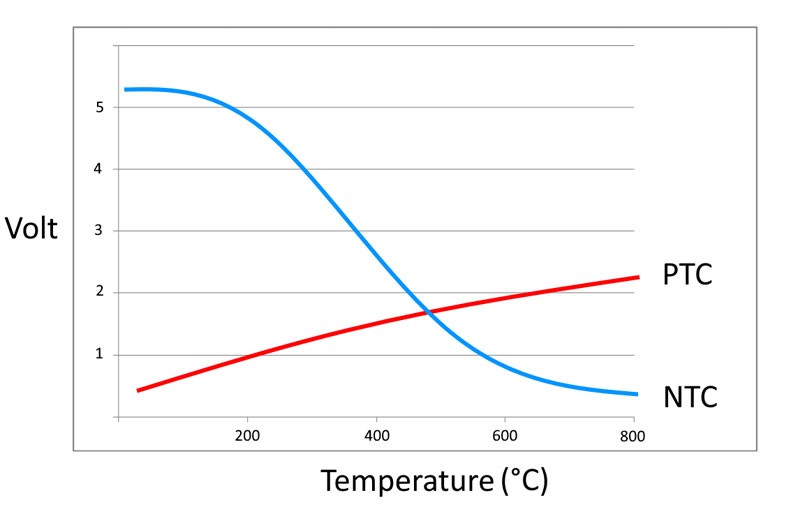
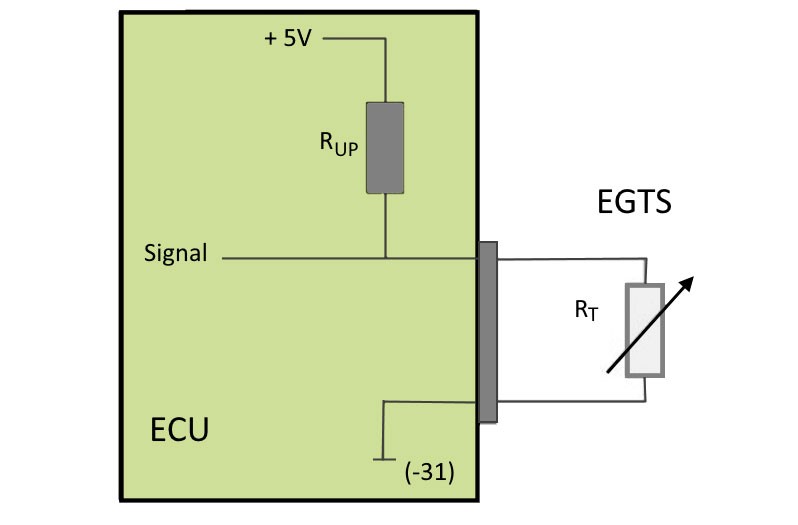
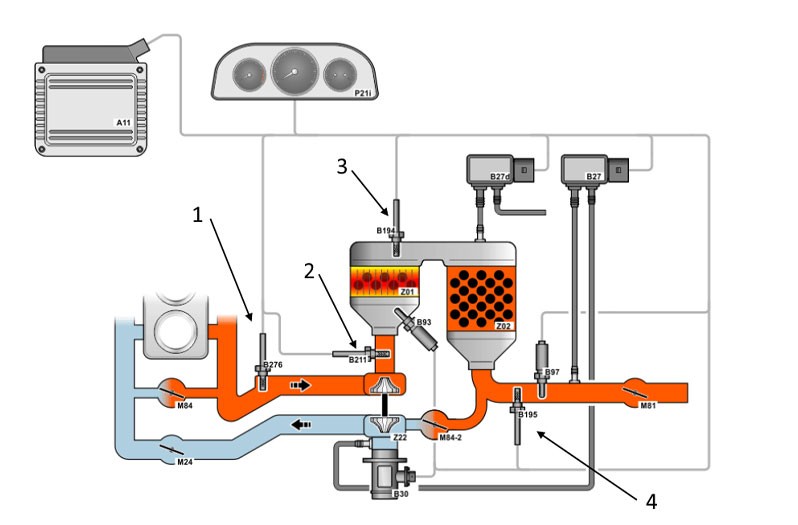
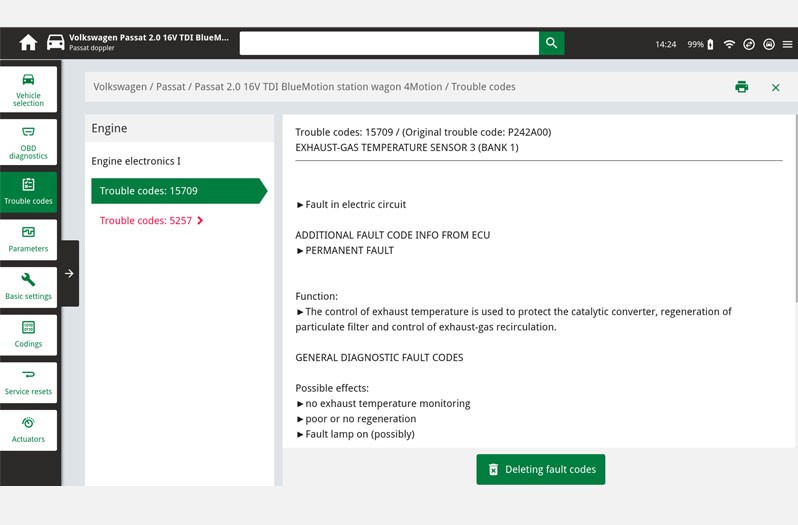
Error code
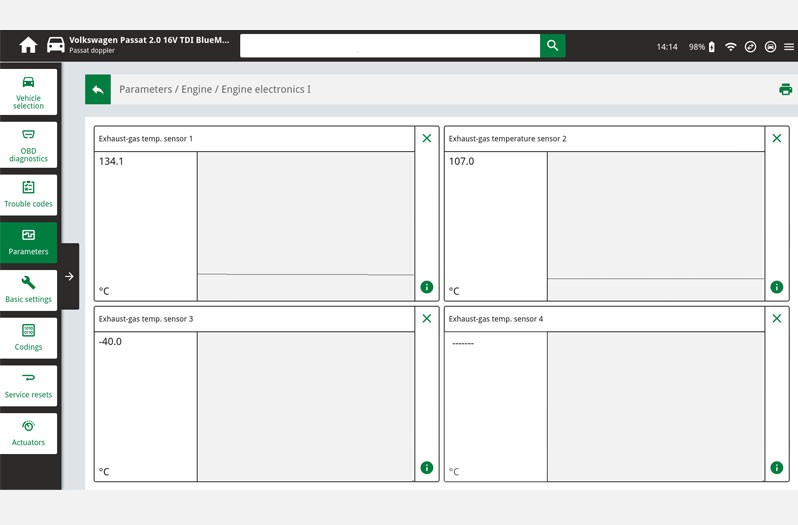
In this function the error codes stored in the error memory can be read out and deleted. In addition, information on the error code can be called up.
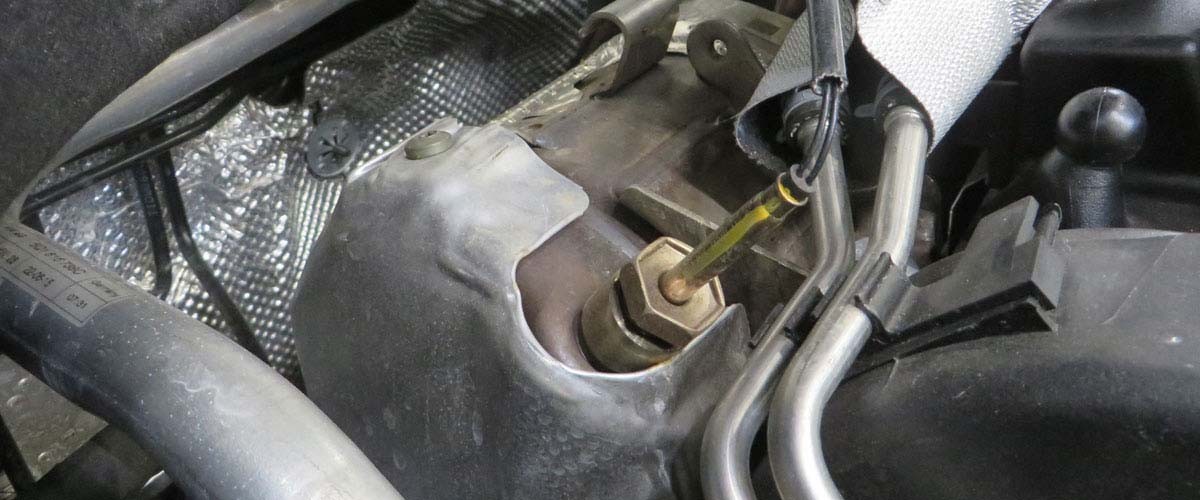
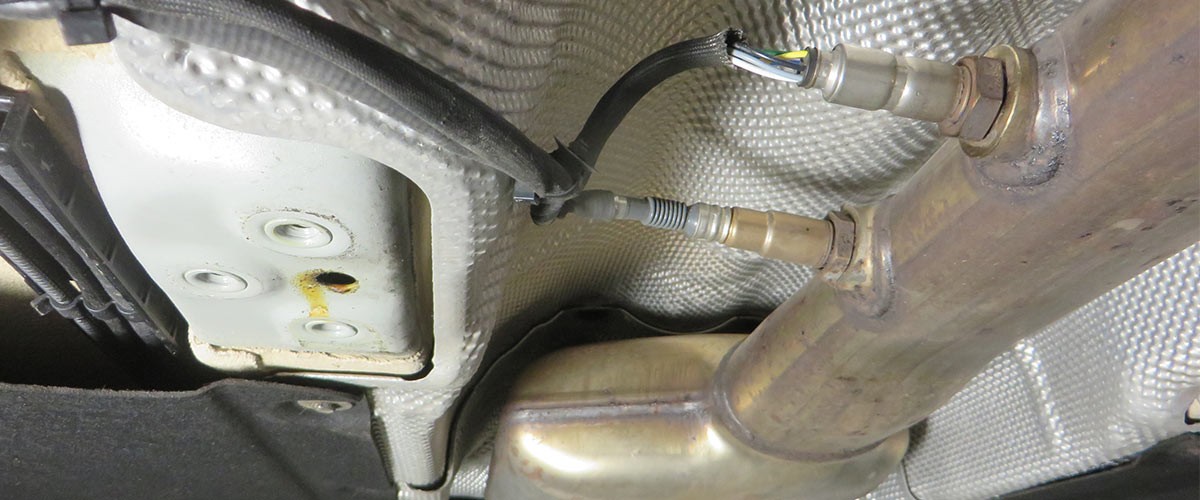
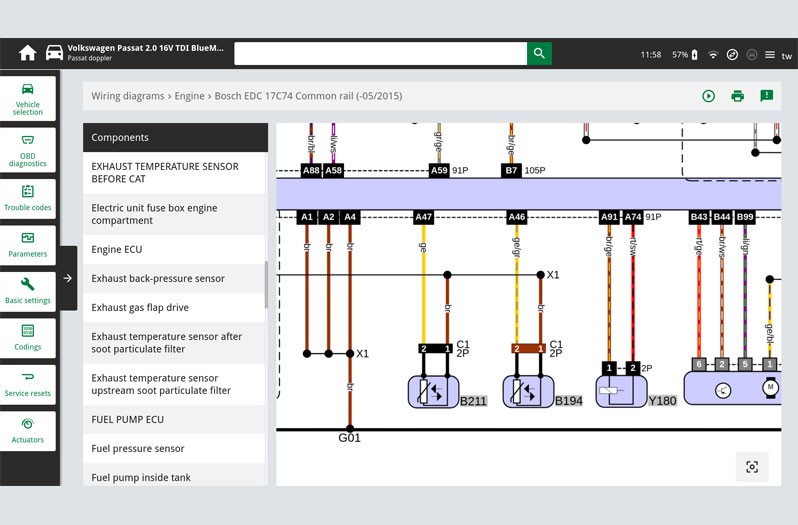
- In our case study the error codes 15709 and 5257 are displayed, codes which indicate a fault in exhaust gas temperature sensor 3.