Signal lights in cars
Signal lights have an important safety function. They demonstrate deceleration and a change in direction of the vehicle, and make the vehicle more visible to other road users when it is dark or during poor visibility. On this page, you can find out how signal lights are structured, and what technology is behind new signal systems. Here you can also find the most common causes of failure for signal lights, tips for troubleshooting, and information regarding important regulations.
Important safety note
The following technical information and practical tips have been compiled by HELLA in order to provide professional support to vehicle workshops in their day-to-day work. The information provided on this website is intended for suitably qualified personnel only.
- 1. Structure
- 2. Function
- 3. Practical tips
- 4. Symptoms
- 5. Troubleshooting
- 6. Good to know
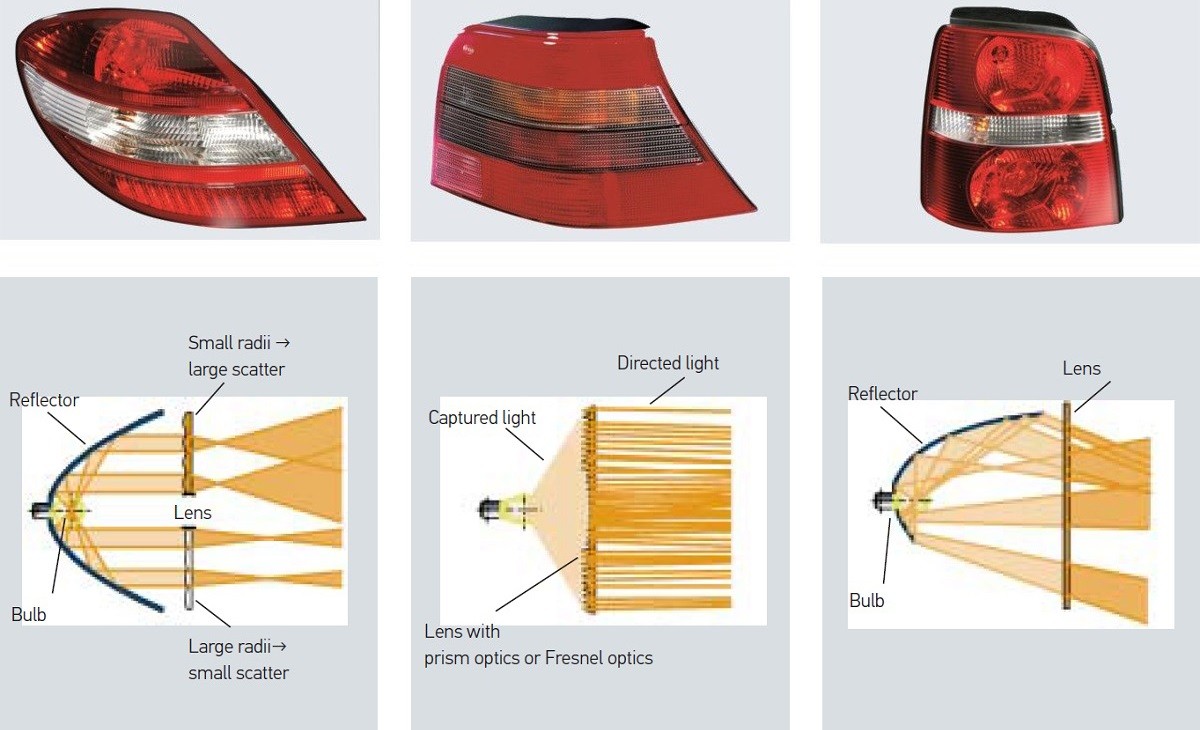
Car indicator signal lights
Exterior lights – whether attached at the front, side or rear of the vehicle – provide information for other road users through their signals and are thus responsible for safety on the roads to a substantial extent.
Asignis® – Adaptives Signal-system
Tips for dealing with signal lights
Faulty signal lights
A faulty signal light can be detected from the following symptoms:
- No signal is emitted for individual functions e.g. stop light. This leads to an increased safety risk, particularly during night-time driving
- The indicator lamp on the dashboard lights up (failure monitor, if present)
- Two lighting functions light up e.g. direction indicator and tail light
Checking signal lights
If a signal light fails, there are always several possible causes. The following points should be noted when troubleshooting:
- Check the light sources and replace if necessary
- Check the bulb holder for corrosion and contact interruption
- Check the voltage supply including fuses
- Check the plug-type connection for corrosion and mechanical damage
- In vehicles with PWM, check the signals with an oscilloscope/diagnostic tester.
Signal light regulations
Due to the scope of the statutory regulations, only the most important are explained here. The following regulations contain all the relevant information about signal lights, their properties, and uses:
76/759/EEC, ECE-R6, StVZO § 54
Direction indicators front, rear, and side
76/758/EEC, ECE-R7, StVZO §§ 51 and 53
Marker lights and tail lights front and rear
77/540/EEC, ECE-R77, StVZO § 51
Parking lights front and rear
ECE R87
Daytime running lights
77/539/EEC, ECE-R23, StVZO § 52
Reversing lights
76/758/EEC, ECE-R7, StVZO § 53
Stop lights
77/538/EEC, ECE-R38, StVZO § 53d
Rear fog lights
76/760/EEC, ECE-R4, StVZO § 60
License plate lamps
ECE R3
Reflex reflectors
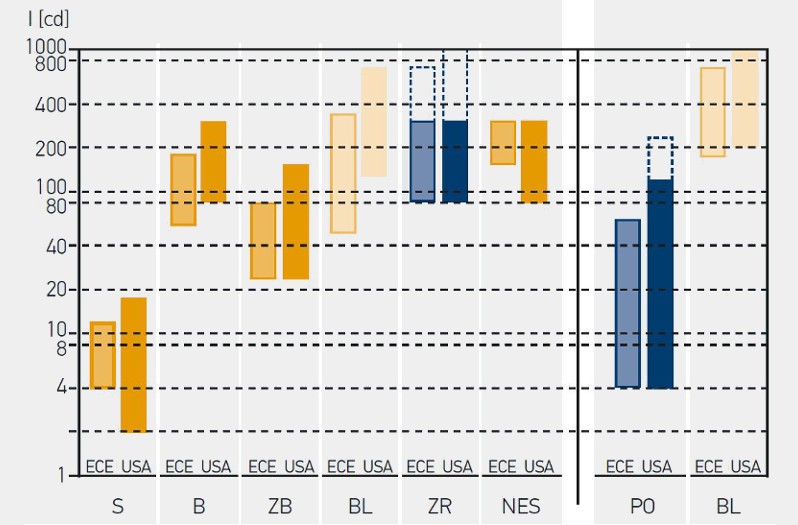
| Direction indicators front, rear, and side | |
| Number at the front | Two |
| Number at the rear | Two or four |
| Number at the side (optional) | One per side |
| Colour | Amber |
| Height position | Between 350 mm and 1500 mm permissible |
| Width position | |
| Side position | Installation height between 350 mm and 1500 mm and max. 1800 mm from the front edge of the vehicle |
| Electrical circuit | An electronic warning flasher unit is made up of a pulse generator which switches the lights on via a relay. In addition, it also has a control circuit which is dependent on current and changes the flashing frequency in the event of light failure. The frequency of the flashing signals is between 60 and 120 per minute. All the direction indicators on the same side of the vehicle have to work synchronously. |
| Switch-on control | Green indicator lamp |
| Miscellaneous | Depending on the requirements, there are different functional controls for monitoring the indicator system (single-circuit, dual-circuit control). |
| Marker lights (passenger vehicles) front | |
| Number | Two or four |
| Colours | White, or amber when main headlamps are amber |
| Mounting | The arrangement is the same as for the front direction indicators. |
| Miscellaneous | Vehicles and trailers over 1600 mm wide require marker lights (to the front). |
| Tail lights | |
| Number | Two or four |
| Colour | Red |
| Height position | Between 350 mm and 1500 mm permissible |
| Width position | Max. 400 mm from the outermost edge of the body. At least 600 mm apart |
| Electrical circuit | No particular specifications |
| Miscellaneous | In the event of dual function (stop and tail light), the luminous intensity ratio of the individual functions must be at least 5 to 1. |
| Rear fog lights | |
| Number | One or two |
| Colour | Red |
| Height position | Between 250 mm and 1000 mm permissible |
| Width position | The distance to the stop light must be at least 100 mm. |
| Electrical circuit | Rear fog lights may only work when low beam, high beam, or fog lamps are switched on. They must be able to be switched off independently of the fog lamps. |
| Switch-on control | Amber, vehicles approved before 1981 also green |
| Miscellaneous | The visible illuminated area must not be more than 140 cm2. The light may only be switched on when visibility is less than 50 m. |
| Rear fog lights | |
| Number | One or two |
| Colour | Red |
| Height position | Between 250 mm and 1000 mm permissible |
| Width position | The distance to the stop light must be at least 100 mm. |
| Electrical circuit | Rear fog lights may only work when low beam, high beam, or fog lamps are switched on. They must be able to be switched off independently of the fog lamps. |
| Switch-on control | Amber, vehicles approved before 1981 also green |
| Miscellaneous | The visible illuminated area must not be more than 140 cm2. The light may only be switched on when visibility is less than 50 m. |
| License plate lamps | |
| Number | Depending on requirements one or two lamps |
| Colour | White |
| Mounting | No particular specifications |
| Electrical circuit | No particular specifications |
| Switch-on control | Amber, vehicles approved before 1981 also green |
| Miscellaneous | The rear license plate must be illuminated in such a way that it can be read at a distance of 25 m. The minimum luminance of the complete surface area must be at least 2.5 cd/m2. |
| Reversing lights | |
| Number | One or two |
| Colour | White |
| Height position | 250 to 1200 mm permitted |
| Width position | No particular specifications |
| Electrical circuit | The circuit only works with the ignition switched on and the reverse gear engaged. |
| Parking lights | |
| Number | Depending on requirements two at the front and two at the rear or one at each side |
| Colour | White |
| Height position | Between 350 mm and 1500 mm permissible |
| Width position | Max. 400 mm from the outermost edge of the body. At least 600 mm apart |
| Electrical circuit | The parking lights must be able to work without other lamps being switched on. |
| Switch-on control | Amber, vehicles approved before 1981 also green |
| Miscellaneous | The parking light function is usually taken over by the tail lights. |
| Side marker lights | |
| Number | Depending on the length of the vehicle |
| Colour | Amber |
| Height position | Between 250 mm and 1500 mm permissible |
| Width position | Max. 3000 mm from the front edge of the vehicle and max. 1000 mm from the rear edge of the vehicle |
| Electrical circuit | No particular specifications |
| Daytime running lights | |
| Number | Two at the front |
| Colour | White |
| Height position | Between 250 mm and 1500 mm permissible |
| Width position | Max. 400 mm from the outermost edge of the body. At least 600 mm apart |
| Electrical circuit | The daytime running lights must switch off automatically if the low-beam headlamps are switched on. |
Installation regulations side view
Installation regulations rear view
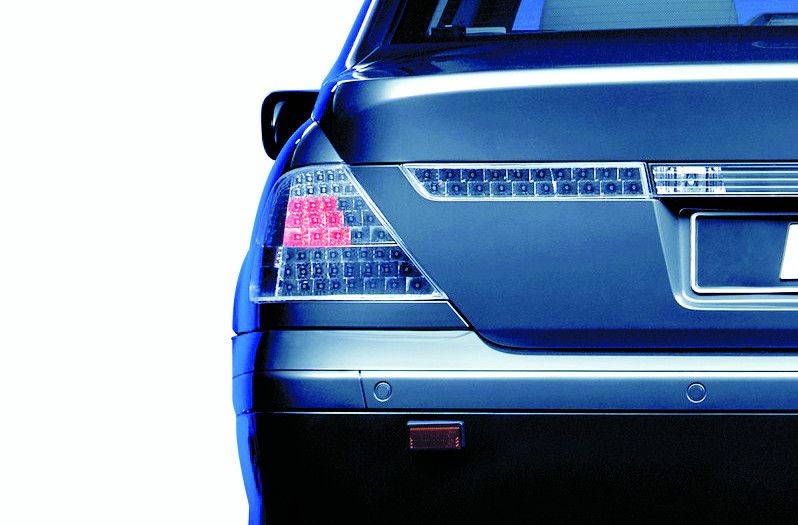
Type approval numbers on signal lights
National and international design and operating regulations apply for the manufacture and testing of vehicle lighting equipment. Special approval marks exist for signal lights and can be found on the light.
One example
The following can be found on a light RS1 IAF 02 E1 Æ 31483:
- R stands for tail light,
- S1 for stop light,
- IA for reflex reflector,
- F for rear fog light and 02 means that the regulation has been revised twice since publication.
These features are integrated in the rear combination lamp:
- The E1 marking means that the light has been approved in Germany.
- The arrow shows which way the light can be installed and therefore always points to the outer edge of the vehicle. If there is no arrow on the light it can be installed at the right or left rear side.
- The five-digit number at the end is the type approval number.
How helpful is this article for you?
Success
Success
Success
Success
Error
Please tell us what you did not like.
Thank you for your feedback!
Wrong Captcha
Something went wrong
Further technical information