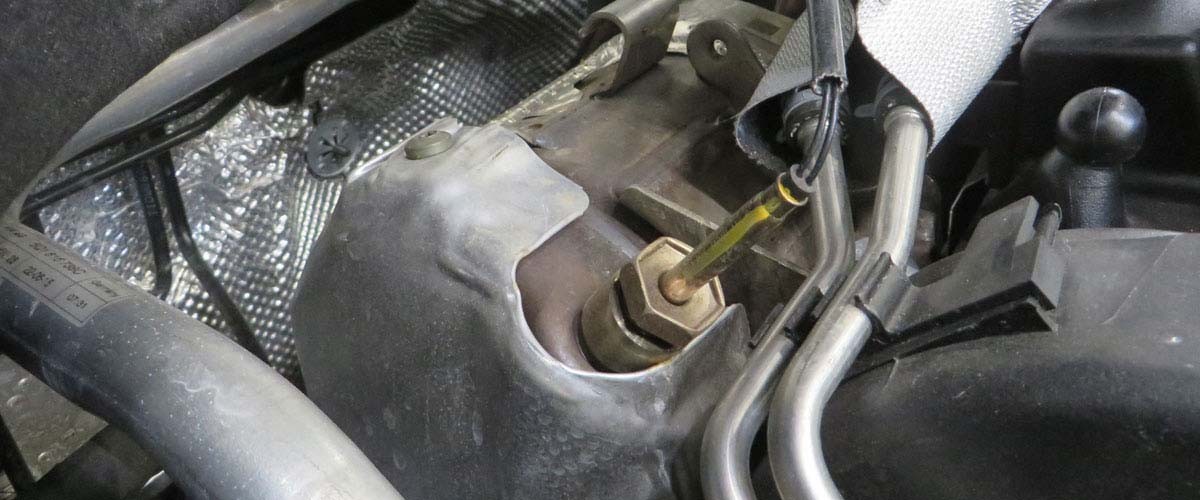
Crankshaft sensor
The crankshaft sensor is one of the key providers of information of the engine control. It detects the speed and position of the crankshaft and forwards this information to the engine control in the form of an electrical signal. On this page, you can find out how crankshaft sensors work, and what must be taken into account when checking them in order to prevent damage.
Important safety note
The following technical information and practical tips have been compiled by HELLA in order to provide professional support to vehicle workshops in their day-to-day work. The information provided on this website is intended for suitably qualified personnel only.
- 1. Functional principle
- 2. Symptoms
- 3. Cause of failure
- 4. Troubleshooting
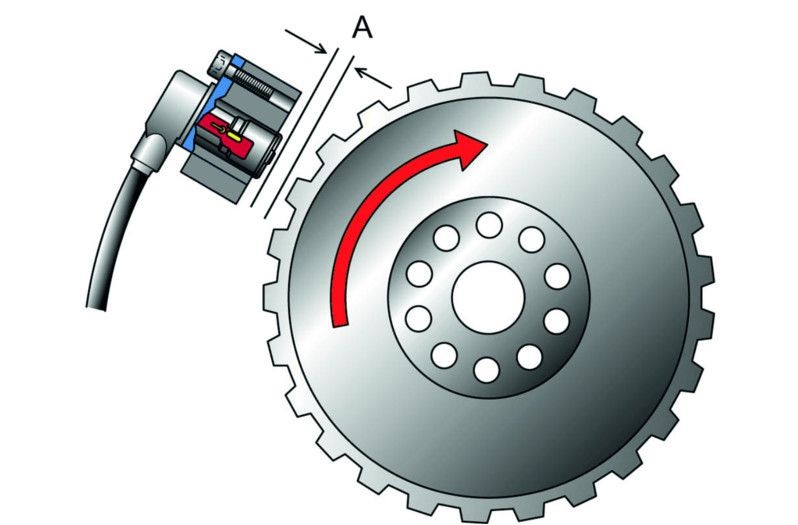
Crankshaft position sensor function
Crankshaft sensor defective
A faulty crankshaft sensor can cause the following symptoms:
- Engine stalls
- Engine standstill
- Problems starting
- Error code is stored
Causes of defective crankshaft sensors
Causes of failure can be:
- Internal short circuits
- Breaks in wiring
- Wiring short circuit
- Mechanical damage to the encoder wheel
- Soiling caused by metal abrasion
Checking the crankshaft sensor
Troubleshooting:
The following procedure is recommended for troubleshooting:
- Read out the fault memory
- Check the electrical connections of the sensor wiring, the connector, and the sensor for correct connection, breaks, and corrosion.
- Watch out for soiling and damage
Direct checks on the crankshaft sensor can be difficult if the exact design type of the sensor is not known. Before the checks, it must be clear whether the sensor is an inductive sensor or Hall generator. It is not always possible to distinguish between the two in terms of appearance. If there are three pins on the connector, no precise statements can be made about the respective type. The specific manufacturer specifications and the specifications in the spare-parts catalog provide further assistance here.
If the design type has not been definitively clarified, an ohmmeter must not be used for the tests. The voltage from the measuring device used for the resistance test could destroy a Hall generator!
Assembly instructions
Make sure that the distance to the encoder is correct and that the sensor is fitted correctly.
How helpful is this article for you?
Success
Success
Success
Success
Error
Please tell us what you did not like.
Thank you for your feedback!
Wrong Captcha
Something went wrong
You might also be interested in