Accelerator pedal sensor
The accelerator pedal sensor transmits the position of the accelerator pedal to the engine control unit. Based on this information, the load requested by the driver can be implemented immediately. On this page we will explain the principle according to which modern pedal travel transmitters operate, and which symptoms indicate a fault in this sensor. You will also find out how accelerator pedal sensors are checked in the workshop.
Important safety note
The following technical information and practical tips have been compiled by HELLA in order to provide professional support to vehicle workshops in their day-to-day work. The information provided on this website is intended for suitably qualified personnel only.
- 1. Functional principle
- 2. Symptoms
- 3. Cause of failure
- 4. Troubleshooting
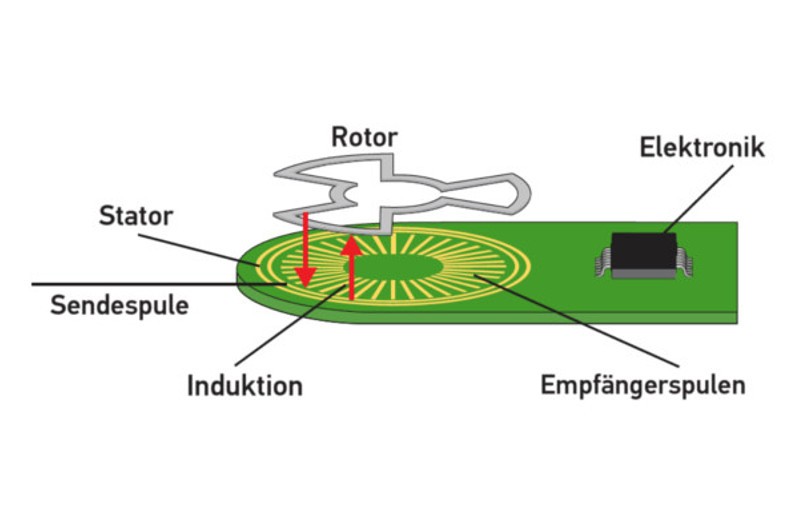
How the accelerator pedal sensor works
Symptoms of a faulty accelerator pedal sensor
If the accelerator pedal sensor fails, the following fault symptoms may occur:
- Increased engine idling speed
- Vehicle does not respond if the accelerator pedal is pressed
- Vehicle switches to "limp-home mode"
- Engine warning light in the cockpit illuminates
Accelerator pedal sensor faulty
A failure could have a number of different causes:
- Damaged cables or connections on the accelerator pedal sensor
- Missing voltage and ground supply
- Faulty electronic evaluation unit in the sensor
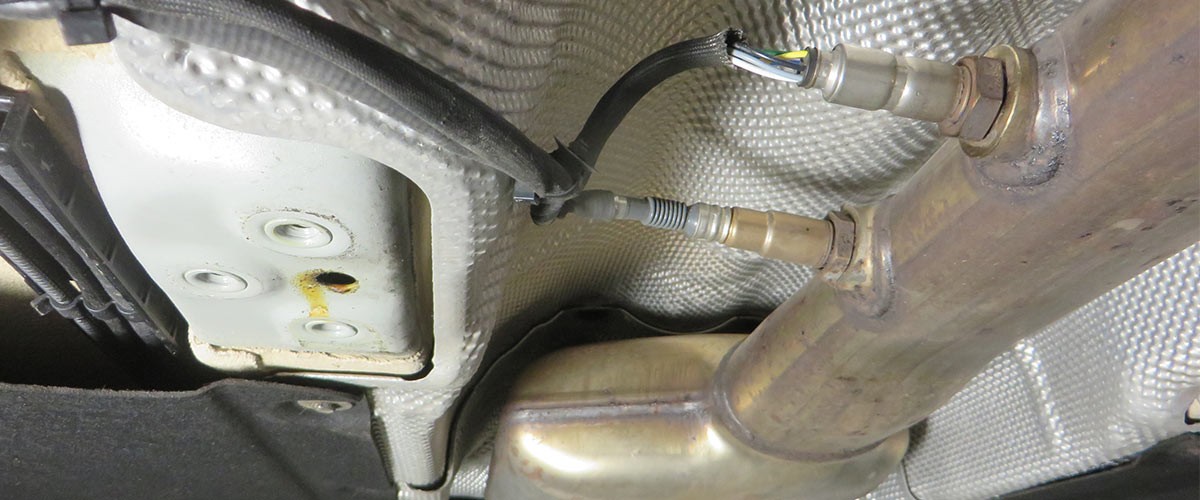
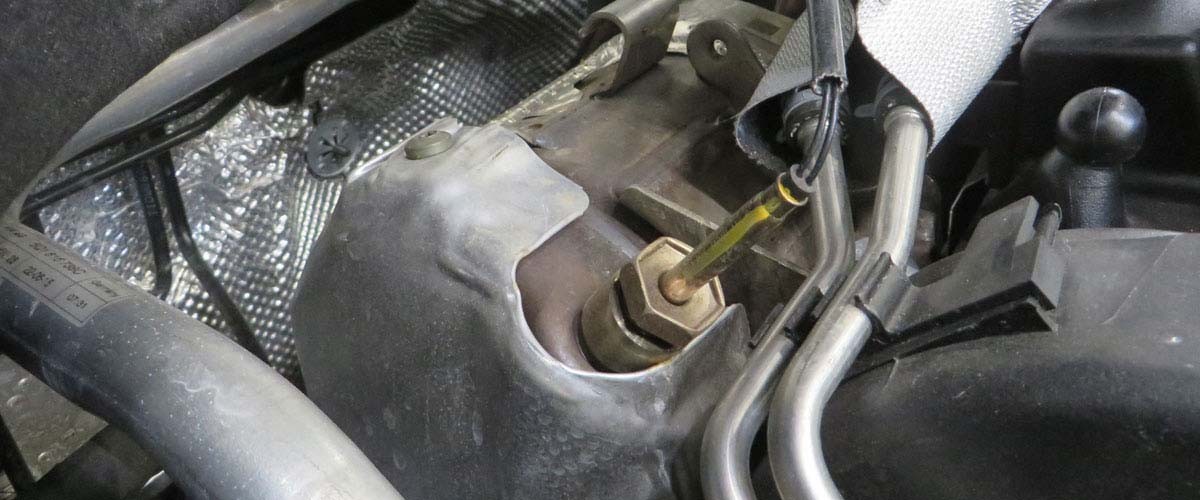
Checking the accelerator pedal sensor
The following test steps should be considered during troubleshooting:
- Read out fault code
- Visual inspection of the accelerator pedal sensor to check for mechanical damage
- Visual inspection of the relevant electrical connections and cables to ensure they are properly fitted and for any damage
- Check of the sensor using an oscilloscope and multimeter
Using the example of a MB A-Class (150) 1.7, the following test steps, technical data, and figures are listed to explain the troubleshooting work.
| Control unit pin | Signal | Test conditions | Reference value |
| C5 blue-yellow | → | Acceleration off | 0 V |
| C5 | → | Acceleration off | 4,5 – 5,5 V |
| C8 violet-yellow | ⊥ | Acceleration on | 0 V |
| C blue-grey | ← | Acceleration on, accelerator pedal released | 0,15 V |
| C9 | ← | Acceleration on, accelerator pedal pressed | 2,3 V |
| C10 violet-green | ← | Acceleration on, accelerator pedal released | 0,23 V |
| C10 | ← | Acceleration on, accelerator pedal pressed | 4,66 V |
| C23 brown-white | ⊥ | Acceleration on | 0 V |
→ output signal ← input signal ⊥ control unit ground
RECOMMENDATION!
The measurements should be performed by two people. The work involved in capturing the signals on the sensor, carrying out various test cycles, and performing diagnostics work on the oscilloscope is difficult for a single person to handle, and it will take them much longer to complete this work.
How helpful is this article for you?
Success
Success
Success
Success
Error
Please tell us what you did not like.
Thank you for your feedback!
Wrong Captcha
Something went wrong
You might also be interested in