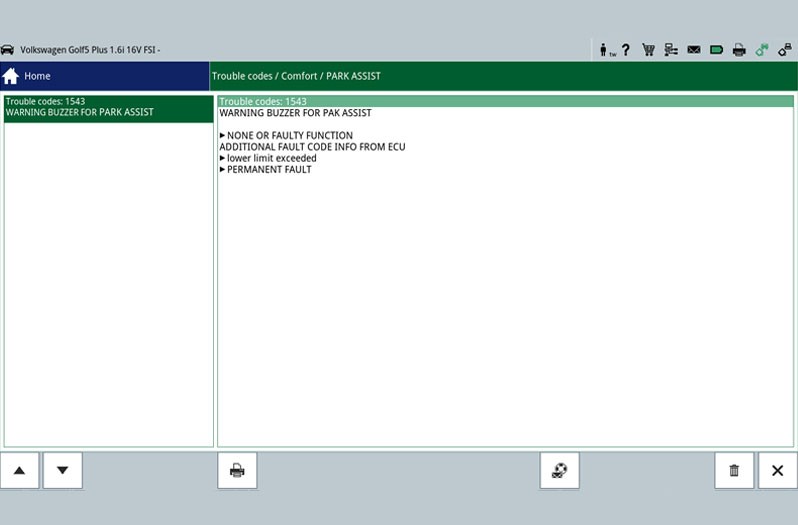
Error code
In this function the error codes stored in the error memory can be read out. For all subsequent troubleshooting, general information regarding possible effects and causes is presented in the error code descriptions.
Important safety note
The following technical information and practical tips have been compiled by HELLA in order to provide professional support to vehicle workshops in their day-to-day work. The information provided on this website is intended for suitably qualified personnel only.
The parking assistant is a driver assistance system that supports drivers during manoeuvring and parking and warns them of obstacles in the immediate vicinity of the vehicle.
The traditional parking aid operates on the basis of ultrasound that is emitted using several sensors. If an obstacle is detected, the driver is informed of this either visually or acoustically. The more ultrasonic sensors that are installed and spread out across the width of the vehicle, the more accurate the measurement result will be. Depending on the vehicle or on the system, LED displays, graphic representations on the screen or purely acoustic signalling devices can be installed to provide the necessary information.
| Acoustic- Parking- System (APS) | Audi |
| Park- Distance- Control (PDC) | Volkswagen, Seat, Skoda, BMW, Toyota, Ford, Mazda, Range Rover, Volvo |
| Parking- Assist- Module (PAM) | Ford |
| Parktronic | Mercedes Benz |
| Parking-Assist-System (PAS) | Volvo |
The following system descriptions and diagnostic information are illustrated using the example of a Golf V Plus. The manufacturer's designation for the purely acoustic parking aid is park distance control (PDC). Because four ultrasonic sensors are installed in the rear bumper, this is referred to as a 4-channel system.
The parking aid is activated as soon as the reverse gear is engaged. The ultrasonic sensors mounted in the bumper emit a package of ultrasonic pulses in combined transmit and receive mode. The signals reflected by an obstacle (echo) are picked up again by the ultrasonic sensors, amplified and then transmitted as digital information to the control unit.
An algorithm in the control unit calculates the distance to the obstacle based on the transit-time difference of the signals. When in receive mode, an ultrasonic sensor also receives signals from neighbouring ultrasonic sensors. The control unit can thus evaluate the signals from several sensors and consequently calculate the minimum distance. The acoustic distance warning system kicks in at a distance of 160cm. The frequency of the sound signal, i.e. the beeping, changes with decreasing distance to the obstacle. If the distance is less than 20cm, a continuous tone sounds.
By disengaging reverse gear or when exceeding a speed of 15km/h, the parking aid is switched off.
The parking aid for the rear section of the vehicle consists of the following components:
Supply voltage 9 -16 volt
Ultrasonic frequency 50kHz - 60kHz
Detection angle: vertical / horizontal 60° +/- 10° degrees
Range 250cm
Temperature range -40 to 85°C
Important information on handling and functioning!
On vehicles with factory-fitted trailer coupling, the PDC system is not activated when a trailer is being towed.
In some cases, smaller objects, bushes, poles or posts may not be recognised and consequently not picked up by the system, which means that without human intervention damage could be caused to the vehicle.
Safety notice!
Drivers bear sole responsibility for parking and for all other manoeuvres!
The electronic parking aid is a driver assistance system, but it cannot replace the due care and attention provided by a human driver. And as a result of physical limitations, dead zones or blind spots can also occur during ultrasonic measurement and object detection if sound reflection is poor. For this reason, drivers always remain responsible for the assessing of obstructions.
The following consequences can occur if the parking aid fails:
The following causes can be responsible for the failure of the parking aid:
The ultrasonic sensors or rather their system functioning is monitored by the relevant higher-level control unit. Any occurring errors are stored in the control unit's error memory and can be exchanged/updated by using a suitable diagnostic unit. With some vehicle models, a warning message can also be displayed on the instrument cluster in the event of a system error.
However, before control unit diagnostics are undertaken, it is first advisable to carry out a visual inspection of the individual system components as part of initial troubleshooting activities.
As part of control unit diagnostics, it is possible to employ the help of various functions and vehicle information as and when needed.
Important
The respective test depth and range of functions can be designed differently depending on the vehicle manufacturer and is dependent on the respective system configuration of the control unit.
In this function the error codes stored in the error memory can be read out. For all subsequent troubleshooting, general information regarding possible effects and causes is presented in the error code descriptions.
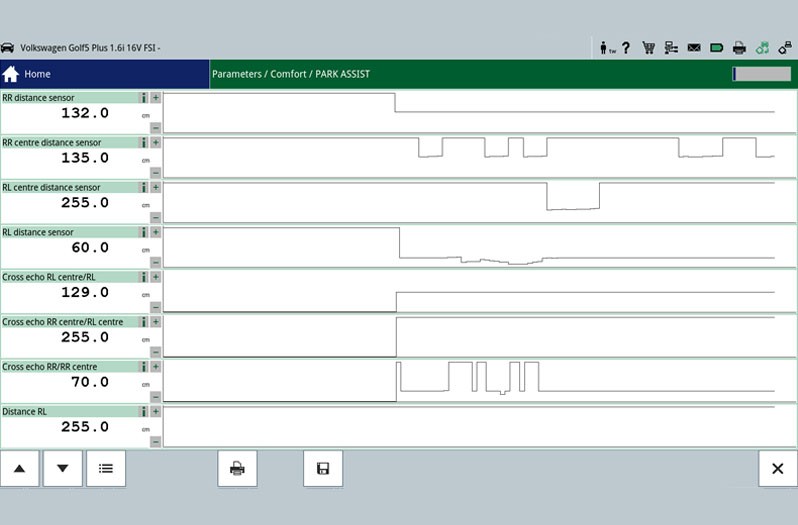
This function enables current measured values from the control unit, such as brake booster pressure or brake pedal position, to be selected and shown.
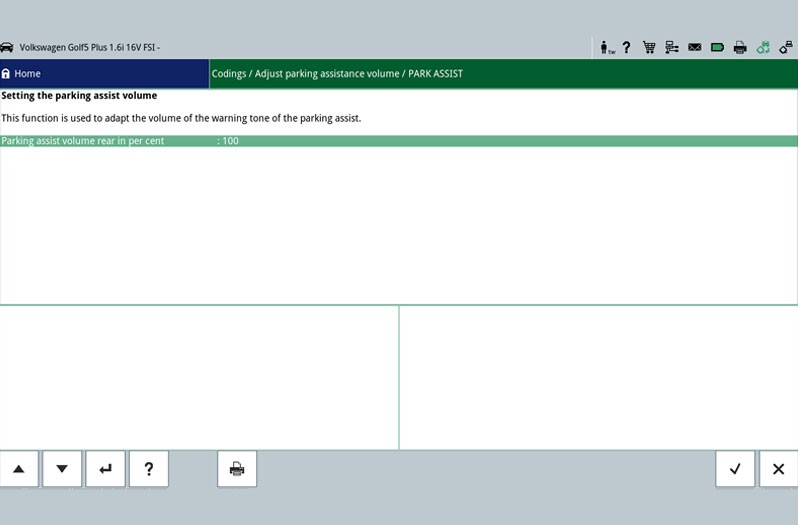
With this function the volume of the parking aid's warning beep can be adjusted.
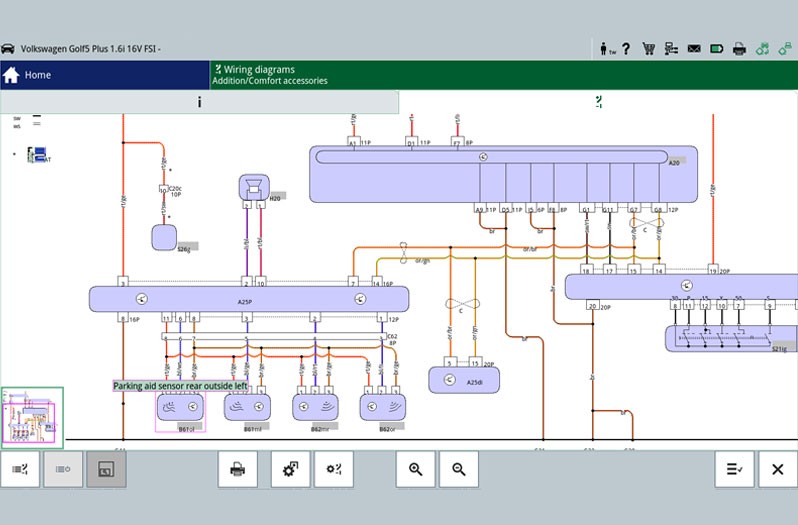
System-specific circuit diagrams can be taken from vehicle information and used for troubleshooting purposes. Here the PIN assignment on the control unit plug or the cable colours can be read off and used for further testing.
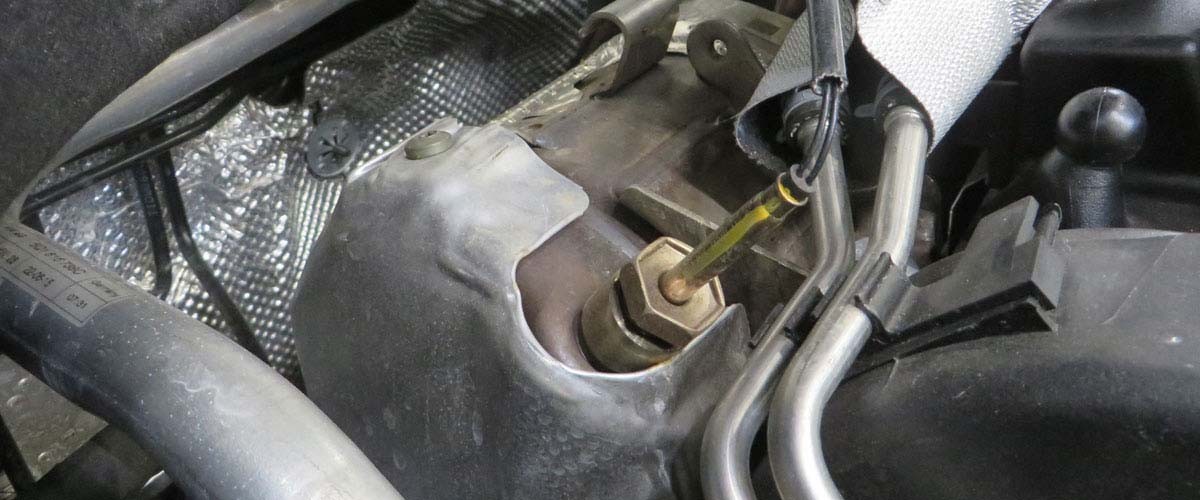
During installation of the ultrasonic sensor, care must be taken to ensure that the decoupling element is correctly seated. If the installation is faulty, send and receive operations may be adversely affected
The ultrasonic sensors in the bumpers must be kept clean and free of ice in order to ensure adequate functioning of the PDC system.
And so as to prevent any damage occurring, cleaning the sensors with a high-pressure cleaner should be avoided.
In the majority of cases, the visible surfaces of the ultrasonic sensors have been painted in the vehicle's colour.
In such cases, the manufacturer stipulates vehicle-specific paintwork guidelines in order to avoid any impaired functioning. So Volkswagen, for example, specifies that the paint thickness on the front and side surface of the membrane must not exceed 125µm.
With regard to this matter, the current, vehicle-specific information provided by each individual vehicle manufacturer should be observed!
Repair notes
How helpful is this article for you?
Success
Success
Success
Success
Error
Thank you for your feedback!
Wrong Captcha
Something went wrong

Benefit from consenting to our cookies ‒ we use cookies to:
By clicking on "I agree", you consent to the placement of cookies.
You can find out more about the cookies used by HELLA websites in our Cookie Policy .
Our cookies do not contain any personal data.
For more information, see our data protection notice.
Great! Just one more Step
Head to your inbox and confirm your email address so that you don’t miss our updates!
Get ready for brand new technical videos, car repair advice, trainings, helpful diagnostic tips, marketing campaigns and much more... delivered straight to your inbox every two weeks!
Sign up for our free HELLA TECH WORLD newsletter to receive the latest technical videos, car repair advice, training, diagnostic tips, and so much more. For April only, grab a 'lost and found' HELLA 2025 Workshop Calendar, whilst stocks last!
Together we can get cars back on the road quickly!
Success
Success
Error
Please note:
You will only be subscribed to the newsletter once you have clicked on the confirmation link in the notification e-mail you will receive shortly!

