Tyre pressure monitoring system (TPMS)
From the end of 2014, all new vehicles have a tyre pressure monitoring system on board as standard. It provides a warning about insufficient tyre pressure and protects the driver against increased fuel consumption and tyre damage. On this page, those interested in technology will find a whole host of details relating to the respective system variants, practical tips for changing tyres, and important information to be taken into account during tyre fitting.
Important safety note
The following technical information and practical tips have been compiled by HELLA in order to provide professional support to vehicle workshops in their day-to-day work. The information provided on this website is intended for suitably qualified personnel only.
Tyre pressure monitoring system
Tyre pressure is an essential safety factor of a vehicle. The most common tyre damage can be traced back to a gradual pressure loss. This is often noticed by the driver of the vehicle when it is too late. Insufficient tyre pressure causes increased fuel consumption and poor driving characteristics. Increased tyre temperature and greater wear are also linked to this. Insufficient tyre pressure may cause the tyre to suddenly burst. This is an extremely high safety risk for all those in the vehicle. This is why tyre pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) have been mandatory since November 2014 for all new vehicles in the EU.
The general parts aftermarket also offers different systems for retrofitting. Tyre pressure monitoring systems monitor the tyre pressure and tyre temperature. Tyre pressure monitoring systems have been on the market for a while, mostly in top-end vehicles. In the USA, they have been mandatory for new vehicles for several years. It is therefore time for all workshop staff to familiarise themselves with this topic. because even during a wheel change, a lack of knowledge about the systems can lead to impairment of the tyre pressure monitoring system.
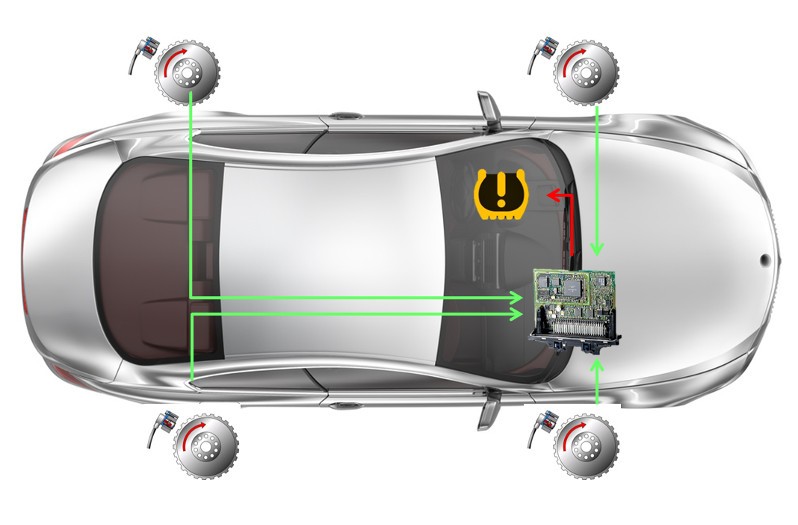
We differentiate between two fundamentally different systems: Indirect and direct tyre pressure monitoring systems.
Indirect tyre pressure monitoring system
Direct tyre pressure monitoring system
What should you pay attention to during wheel and tyre fitting?
Before changing a wheel or tyre, you should always check to what extent the vehicle has a tyre pressure monitoring system. This can be ascertained, for example, from a coloured valve, a coloured valve cap, a symbol in the instrument cluster, or an additional display unit (for retrofitted systems). It is recommended that you ask the customer about any tyre pressure monitoring systems directly during vehicle handover and point out the special features.
Tyre pressure monitoring systems
| System | Manufacturer | Description | Used for |
| TSS | Beru | Tyre Safety System – direct measurement Tyre pressure monitoring system with four separate antennas | Audi, Bentley, BMW, Ferrari, Land Rover, Maserati, Maybach, Mercedes, Porsche, VW, Nutzfahrzeuge |
| SMSP | Schrader, sales in Germany: Tecma | Direct measurement tyre pressure monitoring system with a central antenna | Citroen, Vauxhall, Peugeot, Renault, Chevrolet, Cadillac |
| DDS | Continental Teves | Deflection Detection System – indirect measurement tyre pressure monitoring system | BMW, Mini, Vauxhall |
| TPMS | Continental Teves | Tyre Pressure Monitoring System – direct measurement tyre pressure monitoring system | Vauxhall |
| VDO | BMW, Citroen, Fiat, Ford, Honda, Hyundai, Infiniti, Jaguar, Jeep, Kia, Lada, Lancia, Land Rover, Mazda, Mercedes Bens, Mini, Mitsubichi, Nissan, Peugeot, Renault, Suzuki, Tesla, Volkswagen, Volvo | ||
| Warn Air | Dunlop | Indirect measurement tyre pressure monitoring system | BMW, Mini |
| Tire Guard | Siemens VDO | Direct measurement tyre pressure monitoring system with a sensor which has been permanently integrated into the tyres without a battery | Renault |
| Smar Tire | Sales: Seehase | Direct measurement tyre pressure monitoring system for retrofitting | Universal |
| X-Pressure | Pirelli | Direct measurement tyre pressure monitoring system for retrofitting | Universal |
| Road Snoop | Nokian | Direct measurement tyre pressure monitoring system for retrofitting | Universal |
| Magic Control | Waeco | Direct measurement tyre pressure monitoring system for retrofitting | Universal |
Tyre safety system (tss) beru
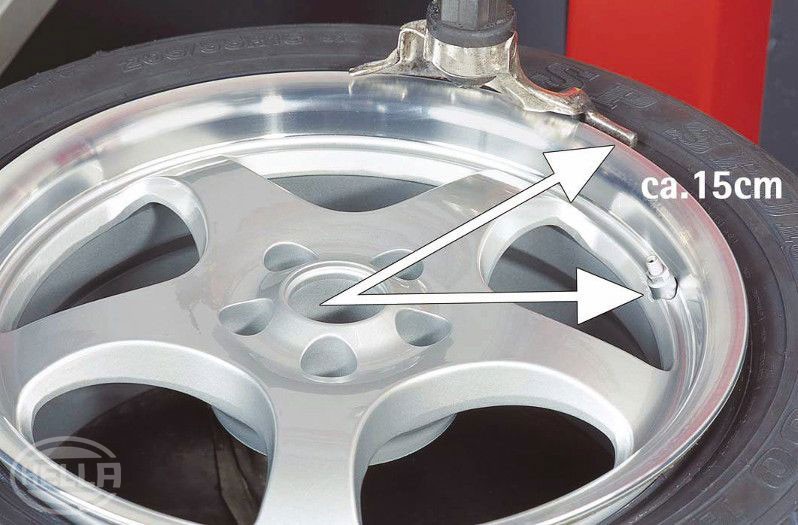
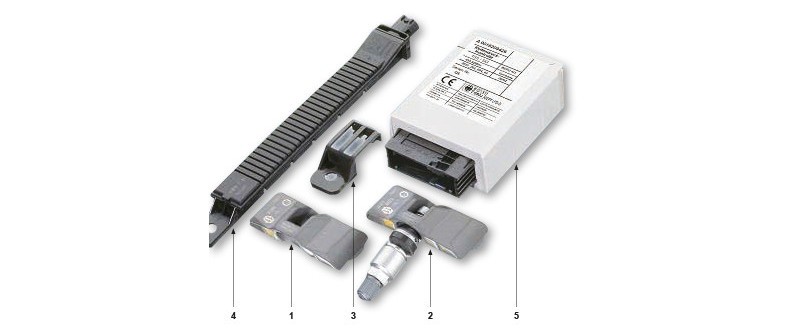
The TSS from Beru is installed in series by many vehicle manufacturers, but is also offered as an accessory for retrofitting. BMW calls the Beru system "RDC" (Reifen Druck Control, or Tyre Pressure Control); at Mercedes and Audi it is the "tyre pressure control system". It comprises four aluminium valves, four wheel electronics systems (wheel sensors), and four antennas, and a control unit (with an additional spare wheel monitoring system, five of each). The wheel electronics and valve are mounted on the rim. The radio receivers are located in the wheel well. For systems installed in series, the display unit is integrated in the instrument cluster.
Following a wheel/tyre change, changing of the wheel position, replacement of the wheel sensor system, or a deliberate change to the tyre pressure (e.g. when the vehicle is fully loaded), the new pressures are taken over by the TSS. For this, all of the tyres must first of all be filled with the prescribed or specially selected pressure. By pressing the calibration button, the values are saved. The system then checks whether the pressures are realistic (e.g. the minimum pressure or the differences between left and right). If the wheels are transported in the boot of the vehicle concerned, for example for seasonal changing of the wheels, they are within range of the control unit. If the wheels being replaced have already been input into the system instead of the usual four (five with spare wheel), the control unit now receives eight or nine signals. In this case, the system reports that it is "not available".
The same thing can happen when unloaded wheels or the wheels of another vehicle (which also has a tyre pressure monitoring system) are located in the vicinity. Please also make the customer aware that the system must then be re-calibrated again. Calibration of the series TSS is vehicle specific. Instructions for this can be found on the web pages of Beru.
PRACTICAL TIP
If the spare wheel is also to be monitored by the tyre pressure monitoring system, following removal, it should be installed again in the precise location it was in before. Especially during an inspection or following a pressure test, for the BMW E60, E65, for example, it should be ensured that the tyre valve is at the 9 o'clock position again following installation of the spare wheel. The receiver only detects signals from the transmitter in this position.
French vehicle manufacturers in particular use the SMSP system from Schrader. This is different in that it only has one radio receiver (antenna).
The position of the wheels is distinguished using colour identification on the valves:
- Green ring = front left
- Yellow ring = front right
- Red ring = rear left
- Black ring = rear right
Following tyre fitting or replacement of a sensor, it may be necessary to code the sensors as a difference in position of the wheels may not be detected with just one antenna or because the wireless connection was interrupted. As the electronics in this system only measure the pressure every 15 minutes during vehicle standstill and only transfer the measured values once an hour to the control unit, for the coding, you need a diagnostic unit as well as a so-called "valve exciter".
It prompts the wheel sensor system to transmit the measured values to the control unit via radio.
PRACTICAL TIP
Following removal of the wheels (e.g. during
brake repairs
) these must be re-installed in the location they were in originally. Tyre pressure monitoring system display faults may otherwise be the result (e.g. Renault Laguna 2).
For almost all tyre pressure monitoring systems, transmission occurs in the frequency range of 433 MHz. This frequency range is also, however, used by radio devices, radio headphones, alarm systems, and garage door drives, for example. Please take this into account in the event of malfunctions with the tyre pressure monitoring system. The current development is toward small active systems without batteries (transponder technology) which are just glued into the carcass or which are integrated into the tyre. These systems operate in the 2.4 GHz range, which is not so susceptible to interference, and can record other information, such as road condition and wear state, in addition to temperature and pressure values.
Today, tyre pressure monitoring systems are as common a part of vehicle equipment as ABS or the air-conditioning system .
For all of the monitoring technologies, one thing should not be forgotten. A tyre pressure monitoring system does not correct the tyre pressure itself and does not provide any information on the age or the tread depth of a tyre. This means that in the future, too, it will be essential to regularly monitor the tyre as the most important connection between the vehicle and the road
Direct tyre pressure monitoring system - example Mercedes-Benz W212 E350
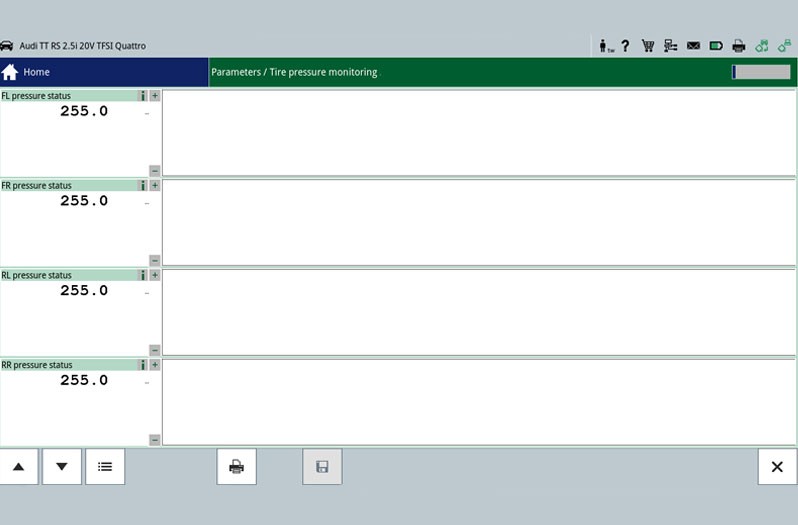
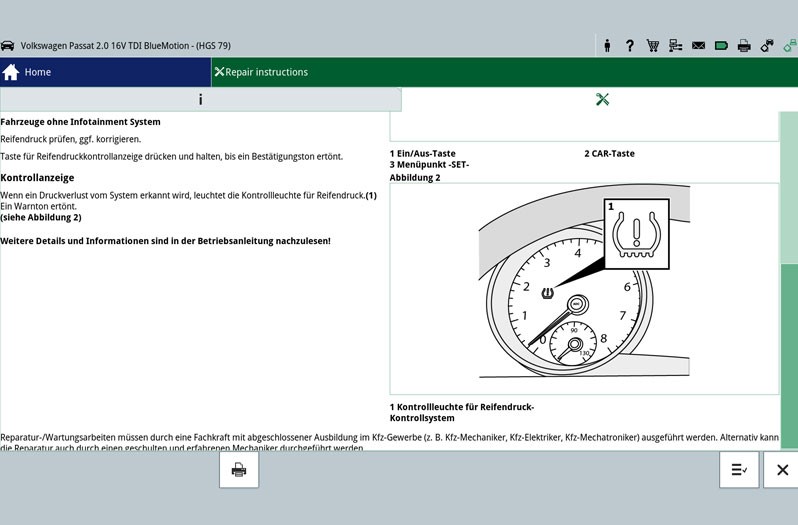
For the purpose of an example, the following information is illustrated using a Mercedes-Benz W 212 E350 featuring direct tyre pressure monitoring system. This vehicle features sensors on all four wheels that forward the tyre pressure to a superordinate system. The tyre pressure monitoring system monitors the tyre pressure using the data from the wheel speed sensors. If a pressure drop is identified on one of the tyres, drivers are visually warned by a notification on the multi-function display indicating "tyre pressure loss" on the instrument cluster.
Adjusting and saving the tyre pressure in the system
In the following cases it is necessary to carry out basic tyre pressure value setting in the system:
- A tyre pressure monitoring system warning message has been activated.
- The tyre pressure has been changed or adjusted.
- Tyres or wheels have been installed in different positions or they have been replaced.
- Battery disconnected or replaced.
The following warning messages appear on the display:
- "Correct tyre pressure". The tyre pressure of at least one tyre is too low and must be re-inflated from time to time
- "Check tyre pressure". The tyre pressure at one or more tyres has dropped significantly
- "Caution: tyre faulty". The tyre pressure at one or more tyres has suddenly dropped significantly
Important!
With regard to this, please always observe the respective maintenance and repair notes provided by the vehicle manufacturer
Indirect tyre pressure monitoring system - example: Mazda CX-5
The following information is illustrated using a Mazda CX-5 featuring indirect tyre pressure monitoring system as an example. The system records the tyre pressure of all four wheels. The ABS control unit determines the tyre pressure on the basis of the data from wheel speed sensors. Drivers are visually and audibly warned if a drop in pressure is detected at one of the tyres. The system must be initialised with the prescribed tyre pressure to guarantee the system operates correctly.
Adjusting and saving the tyre pressure in the system
Re-initialise the system in the following cases.
- Tyre pressure has been corrected.
- One of the tyres has been replaced.
- The position of tyres on the vehicle has been changed.
- The ABS control unit has been replaced or disconnected.
- The battery has been disconnected or replaced.
- The tyre pressure monitoring system warning light is on.
Causes of failure
Warning messages may be output in the following cases because the system may identify changes to the tyre condition.
- A tyre pressure value significantly above the prescribed value has been set
- The wheel and tyre combination does not meet vehicle manufacturer specifications
- Use of a space saver spare wheel or snow chains
- Aggressive driving style, severe acceleration or braking on routes with many corners
- One-sided loading as a result of having overloaded one side of the vehicle
Important!
With regard to this, please always observe the respective maintenance and repair notes provided by the vehicle manufacturer.
EU legislation on tyre pressure monitoring
On March 10, 2009 the European Parliament in Strasbourg officially adopted a proposed directive (EC no. 661/2009) put forward by the Commission to make motor vehicle homologation easier in Europe. In this process, the directive also included a mandatory introduction of previously mentioned technologies including a tyre pressure monitoring system (TPMS). "Category M1/M1G vehicles shall be equipped with an accurate tyre pressure monitoring system capable of outputting an in-car warning to the driver when a loss of pressure occurs in any tyre, in the interests of optimum fuel consumption and road safety. The implementation process was carried out in stages: from November 2012 a tyre pressure monitoring system has been mandatory in all newly homologated vehicle types and this has applied to all newly registered vehicles from November 2014.
How helpful is this article for you?
Success
Success
Success
Success
Error
Please tell us what you did not like.
Thank you for your feedback!
Wrong Captcha
Something went wrong
You might also be interested in