Charging indicator lamp flickers
| Cause: | Remedy: |
| V-belt too loose | Tighten V-belt |
| Setting of the contacts incorrect or the control unit resistor burnt out (Only with contact control units) | Adjust contacts, replace resistor or control unit |
The alternator supplies all electrical components in the vehicle with electricity. Should the alternator lose its full functionality, the electronics will fail after a certain period – the battery will no longer be charged, and the vehicle will no longer be roadworthy. In order that this does not happen, any faults should be detected in good time. We therefore provide you with various problem descriptions and detailed solutions in the following
Important safety note
The following technical information and practical tips have been compiled by HELLA in order to provide professional support to vehicle workshops in their day-to-day work. The information provided on this website is intended for suitably qualified personnel only.
The alternator is usually composed of the following components:
The stator with three-phase winding is mounted in the alternator housing. Claw poles, excitation winding, fan and slip rings are mounted on the shaft of the alternator rotor. The pulley is mounted on the front of the external part of the shaft. The electronic control unit with carbon brush brackets is attached in the rear area of the alternator.
The following symptoms may indicate a fault in the alternator:
An alternator malfunction can have different causes. The cause is not always due to an internal alternator fault, such as a faulty winding, rotor, rectifier or control unit. Before replacing the alternator, additional components should be considered as a cause of failure and checked.
When performing troubleshooting on the alternator, the following fundamental rules are to be observed:
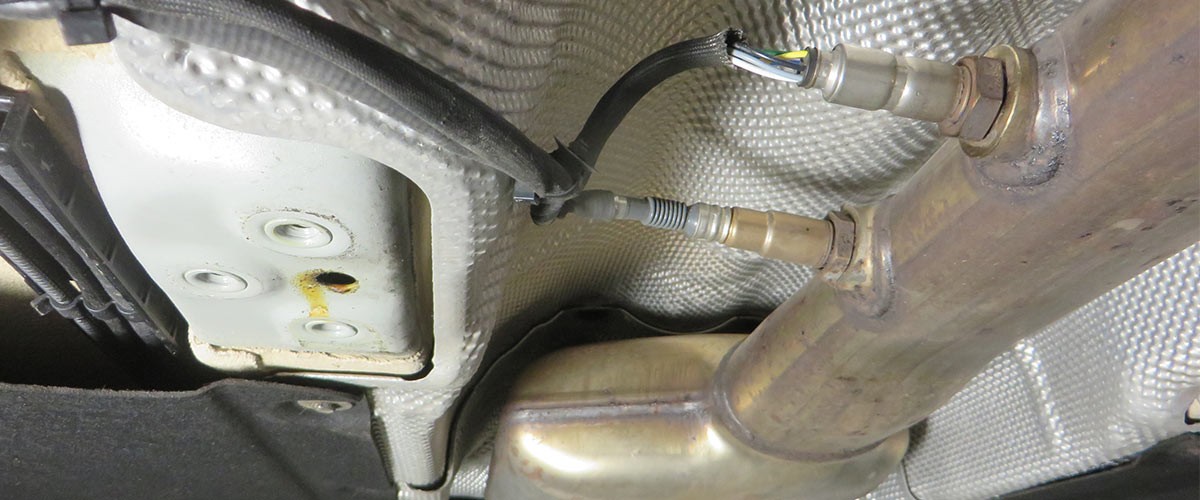
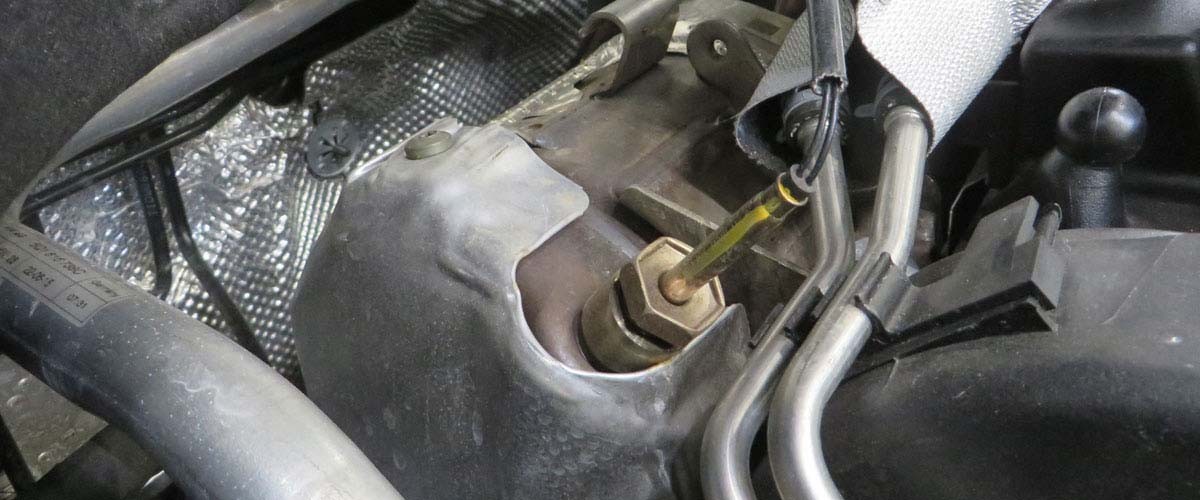
A multimeter and a clip-on ammeter are required for troubleshooting. Please also refer to the technical info: " Ground (31) "
Notice
When performing welding work on the vehicle and when removing or installing the alternator, the battery must be disconnected
| Cause: | Remedy: |
| V-belt too loose | Tighten V-belt |
| Setting of the contacts incorrect or the control unit resistor burnt out (Only with contact control units) | Adjust contacts, replace resistor or control unit |
| Cause: | Remedy: |
| Cable D+/61 has a short circuit to frame |
|
| Control unit faulty | Replace control unit |
| Check alternator and repair or replace if necessary |
| Cause: | Remedy: |
| Contact resistance in the charging current circuit or in the cable for the indicator lamp | Check cable and connections, and replace if necessary |
| Control unit faulty | Replace control unit |
| Alternator faulty | Check alternator, repair or replace if necessary |
| Cause: | Remedy: |
| Battery discharged or faulty | Charge battery, check, replace if necessary |
| Cables or connections damaged, loose or oxidized | Check cables and connections, attach, replace if necessary |
|
|
| Short circuit of a positive diode | Immediately disconnect battery or B+ (otherwise discharge in situ) and repair/replace alternator |
| Oxide coating on the slip rings, break in the rotor winding | Repair/replace alternator |
| Indicator lamp faulty | Replace indicator lamp |
| Cause: | Remedy: |
| V-belt too loose | Tighten V-belt |
| Cables or connections loose, damaged, or oxidized | Check cables and connections between battery and alternator and the respective ground connection, replace if necessary |
| Battery faulty | Charge battery, check, replace if necessary |
| Control unit faulty | Replace control unit |
| Check alternator, repair or replace if necessary |
How helpful is this article for you?
Success
Success
Success
Success
Error
Thank you for your feedback!
Wrong Captcha
Something went wrong


Benefit from consenting to our cookies ‒ we use cookies to:
By clicking on "I agree", you consent to the placement of cookies.
You can find out more about the cookies used by HELLA websites in our Cookie Policy .
Our cookies do not contain any personal data.
For more information, see our data protection notice.
Great! Just one more Step
Head to your inbox and confirm your email address so that you don’t miss our updates!
Get ready for brand new technical videos, car repair advice, trainings, helpful diagnostic tips, marketing campaigns and much more... delivered straight to your inbox every two weeks!
Sign up for our free HELLA TECH WORLD newsletter to receive the latest technical videos, car repair advice, training, diagnostic tips, and so much more. For April only, grab a 'lost and found' HELLA 2025 Workshop Calendar, whilst stocks last!
Together we can get cars back on the road quickly!
Success
Success
Error
Please note:
You will only be subscribed to the newsletter once you have clicked on the confirmation link in the notification e-mail you will receive shortly!
