Visual inspection
- Check all cable connections and plug contacts for correct routing and contacting.
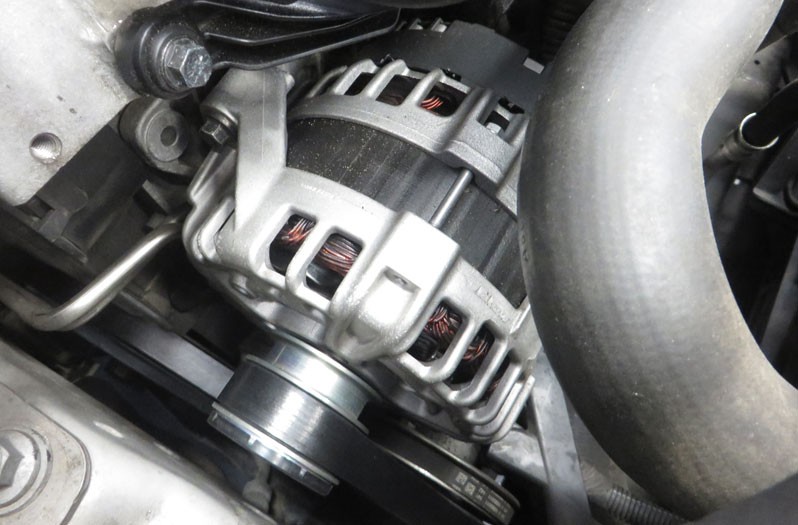
Check alternator drive belt for correct tension and any cracks
Important safety note
The following technical information and practical tips have been compiled by HELLA in order to provide professional support to vehicle workshops in their day-to-day work. The information provided on this website is intended for use by suitably qualified personnel only.
Multi-function regulators offer the following additional functions:
In battery monitoring, the charging voltage of the battery is monitored via "S” connection, which is usually connected directly to the positive battery pole. The direct connection to the battery has the advantage that the existing voltage difference between alternator "+" and battery "+" is taken into account. This means that the charging voltage can be adapted even better to the battery voltage.
With the load control, it is possible to control the power of the alternator during the starting process and when the engine is running. This means that, during the starting process and directly after the engine start, the alternator does not output any current. This prevents the starting process from being prolonged by the full power (braking torque) of the alternator. If there are increased demands during the journey, leading to an increase in torque at the alternator, these are not passed on directly to the engine. The load response slowly increases the power output of the alternator.
The multi-function regulator also controls the pre-excitation current. After switching on the ignition, the regulator output stage starts to cycle in the set clock ratio. The alternator receives information that the ignition is switched on via connection terminal "L". The alternator control lamp remains on while the pre-excitation is active. The evaluation of the phase voltage identifies that the alternator is rotating. If pre-excitation is missing, e.g. due to a faulty plug contact, the emergency mode ensures excitation of the alternator. The idle current cut-off reduces the current consumption of the regulator as much as possible when the ignition is switched off.
If the battery monitoring line to battery "+" is disconnected, an "emergency regulation" takes place via the "B+" connection on the alternator. To protect the regulator against overheating, the temperature is measured on the IC. If the temperature rises too high, the controller voltage is reduced
“L” = The “L” connection has several functions. The "L" connection is used to display the alternator function and any faults that have occurred. The control lamp is actuated via the lamp output stage. Consumers can also be connected via a relay output stage. The consumers should only be switched on when the alternator has reached its full output in fault-free operation. For this, the "L” connection provides an output current via the relay output stage. To detect faults, all signals are constantly evaluated by the regulator and any faults that occur are detected. A fault is indicated by the control lamp turning on via the lamp output stage. The lamp and relay output stages are protected against overload and short circuits. Here, the lamp output stage is active during alternator pre-excitation or when a fault is detected. The relay output stage for connecting the consumers is active during fault-free alternator operation when the lamp output stage is inactive.
"S" = The "S" connection is connected directly to battery "+" to measure the battery voltage as an actual value.
"DFM" = The "DFM” connection (DF monitor) facilitates recording the alternator’s present utilisation status. This makes it possible to react to certain situations, such as raising the idle speed or switching off consumers that are not required. The signal curve of "DF" can be picked up at the "DFM" connection.
"W" At the "W" connection, it is possible to pick up the voltage signal of an alternator phase.

Measure the alternator voltage/alternator current at the battery (observe manufacturer's specifications, differences between manufacturers). Carry out measurements at idle speed and increased engine speed, without and with consumers connected.
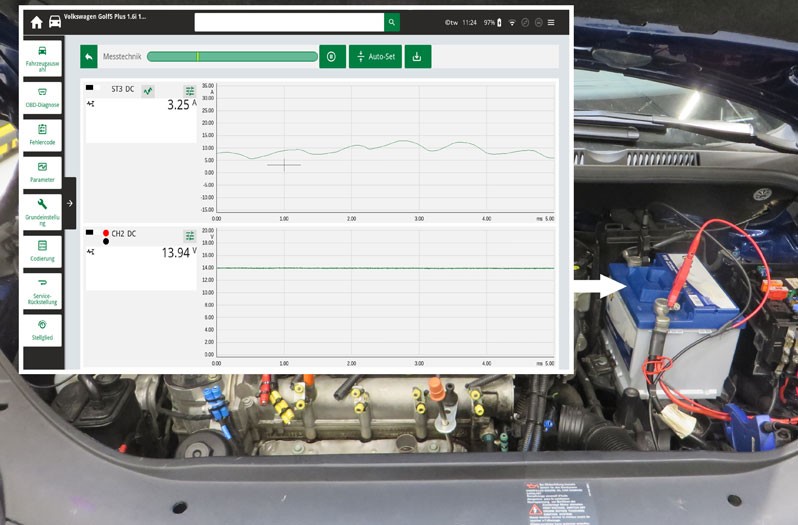
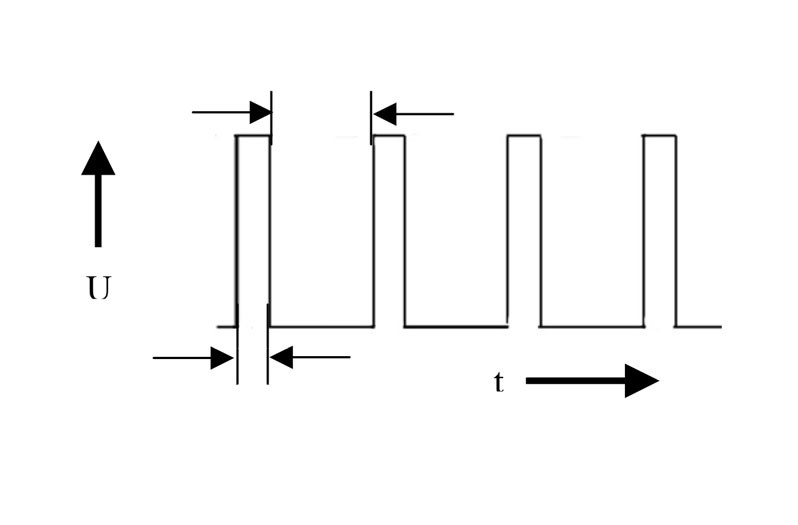
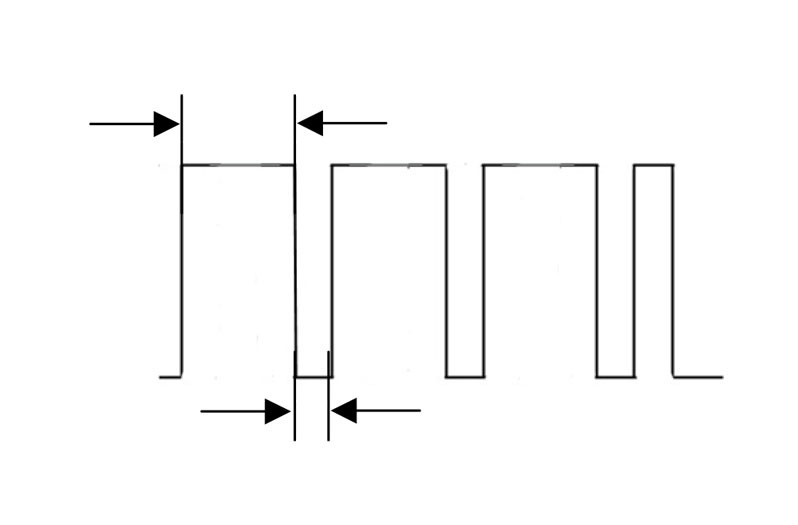
Record the signal at the DFM connection with the oscilloscope. The signal shown reflects the duty cycle of the excitation current. Depending on the load condition of the alternator, the duty cycle must change.
Link to tip
Here you will find tips and remedies for specific symptoms and causes for the failure of a defective alternator . In addition, we show you on this page how to check the charging system , such as carrying out a visual inspection before diagnosis, testing the batteries, performing the alternator test and testing with the diagnostic device. You can find more product information about starters and alternators from Hella here
How helpful is this article for you?
Success
Success
Success
Success
Error
Thank you for your feedback!
Wrong Captcha
Something went wrong

Benefit from consenting to our cookies ‒ we use cookies to:
By clicking on "I agree", you consent to the placement of cookies.
You can find out more about the cookies used by HELLA websites in our Cookie Policy .
Our cookies do not contain any personal data.
For more information, see our data protection notice.
Great! Just one more Step
Head to your inbox and confirm your email address so that you don’t miss our updates!
Get ready for brand new technical videos, car repair advice, trainings, helpful diagnostic tips, marketing campaigns and much more... delivered straight to your inbox every two weeks!
Sign up for our free HELLA TECH WORLD newsletter to receive the latest technical videos, car repair advice, training, marketing campaigns and diagnostic tips.
Together we can get cars back on the road quickly!
Success
Success
Error
Please note:
You will only be subscribed to the newsletter once you have clicked on the confirmation link in the notification e-mail you will receive shortly!
