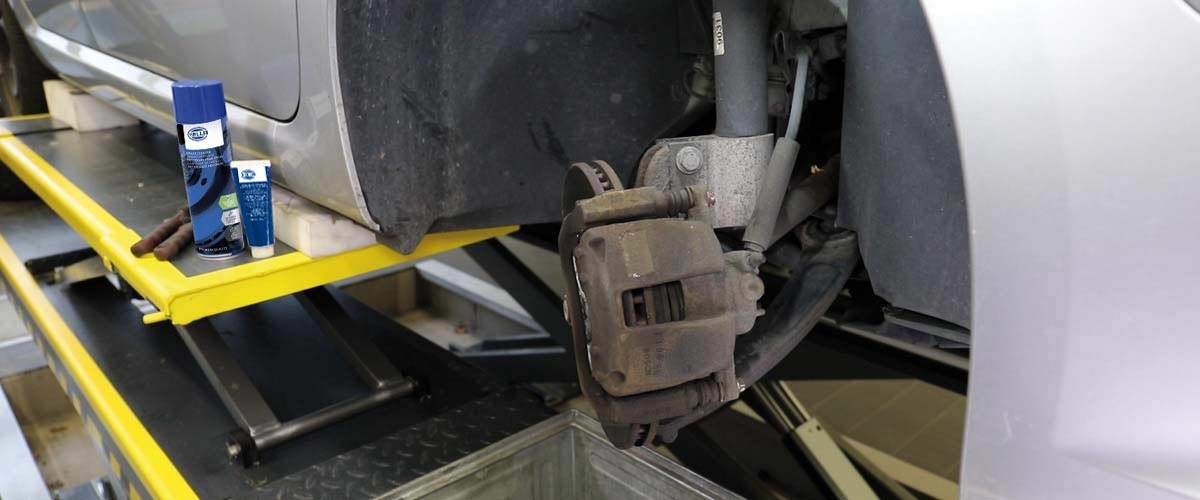
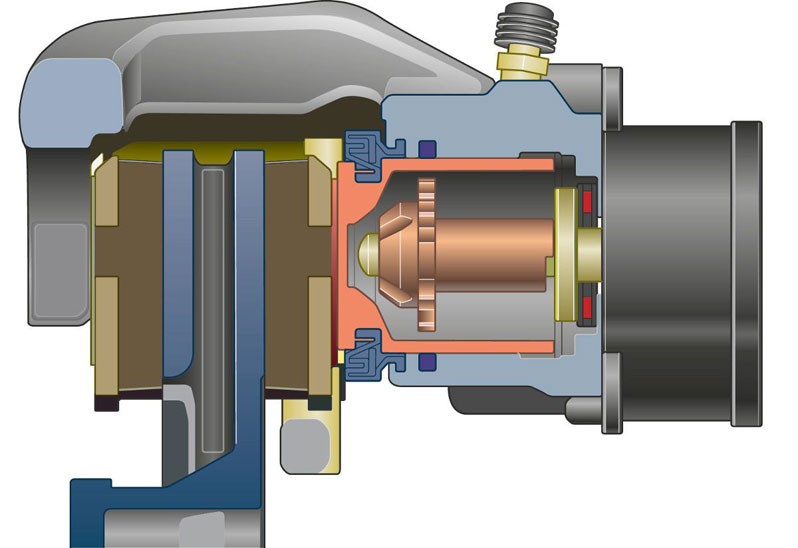
The parking brake mechanism on Audi vehicles comprises a DC motor, a wobble plate gear, and a spindle. The components are attached directly to the rear brake calipers and enable the rotation of the motor to be converted into small brake piston lifting movements. The DC motor powers the wobble plate gear via a belt drive.
The drive motor speed is reduced for the first time here. Due to the belt drive ratio, the speed is reduced to 1:3. The wobble plate gear then reduces the speed further. The speed at the gear output has been reduced by a factor of 147 relative to the drive speed of the DC motor. A spindle directly powered by the wobble plate gear converts the rotation into a lifting movement.
The brake piston houses a cylinder that can move back and forth inside the piston. In order to prevent the cylinder in the piston from turning, it is surface-ground in two locations. A nut is press-fitted to the cylinder front end, and the nut moves on the spindle thread as soon as the spindle rotates. A Hall generator measures the number of DC motor revolutions and passes it on to the control unit, which uses the information to calculate the lift path.
When the parking brake is applied, the rotation of the spindle moves the nut forward. The cylinder then presses the brake pads to the brake disc via the brake piston.
When the parking brake is released, the nut on the spindle is turned back and the brake piston is relieved. As the sealing ring recovers its shape, the brake piston is moved back as is the case after regular braking.
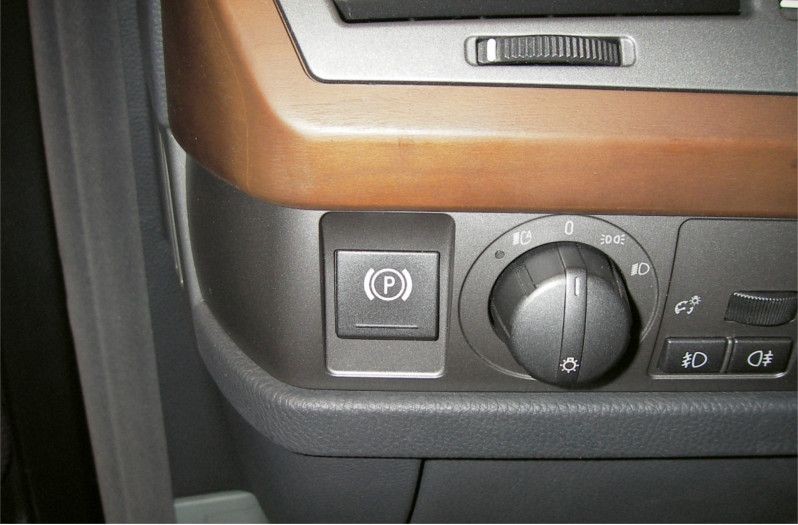
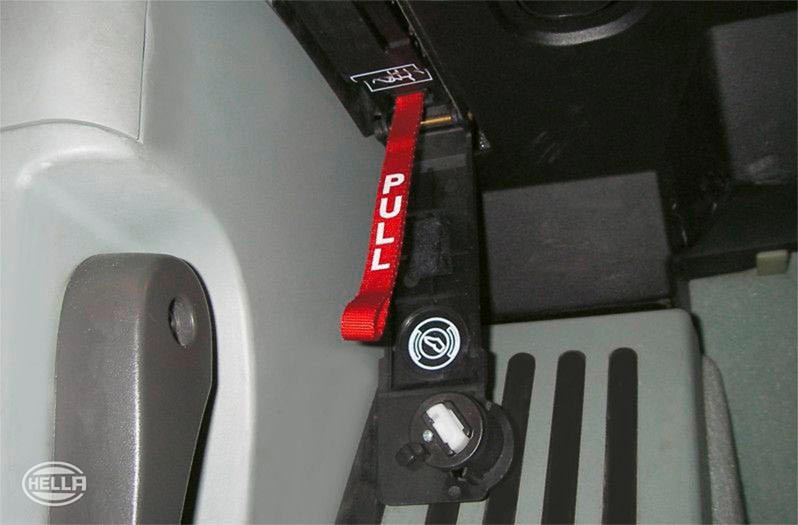
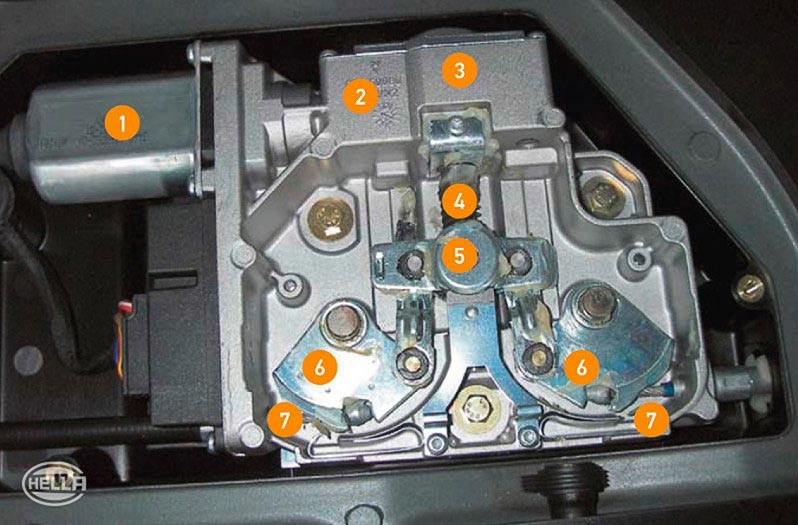
The overall system also comprises a control unit with integrated tilt angle sensor, the indicator lamps, and the switch in the center console.
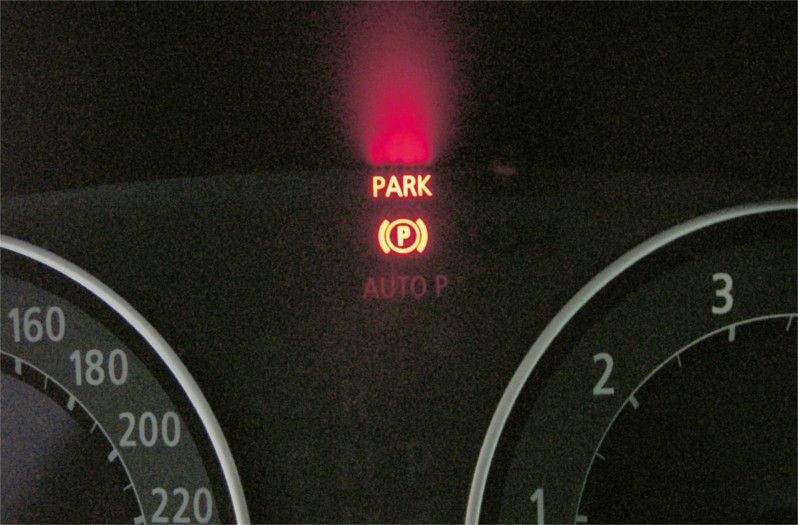
The parking brake is activated by pulling the switch and released by pressing the switch. The indicator lamp in the instrument panel and switch indicates that the parking brake has been activated. Please note that the parking brake can also be activated with the ignition switched off. However, it can only be released with the ignition switched on.