Brake line and hand brake cables
Brake lines, brake hoses, and hand-brake cables all have one thing in common: They transfer the actuation force to the wheel brakes either hydraulically or mechanically. This page explains what requirements are placed on brake lines, brake hoses, and hand-brake cables, how to identify damage to these components, and the important points to bear in mind when replacing them to ensure the safety of the brake system at all times.
Important safety note
The following technical information and practical tips have been compiled by HELLA in order to provide professional support to vehicle workshops in their day-to-day work. The information provided on this website is intended for suitably qualified personnel only.
Brake line and hand brake cables
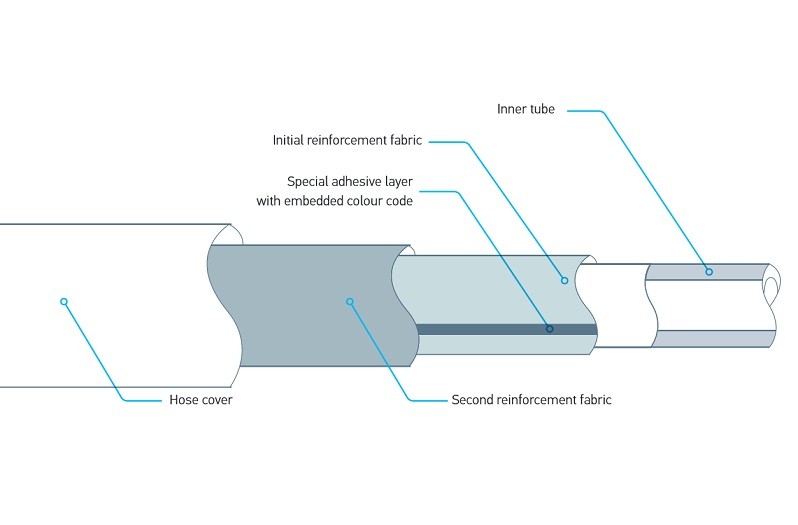
In hydraulic brake systems, brake hoses and brake lines are used to transfer brake fluid. Brake lines connect the actuation device such as the brake master cylinder to the hydraulic components of the wheel brake. Brake hoses are used as flexible connecting pipes in all moving areas between the body and chassis.
With the integration of ABS, ESP, and TCS systems in modern vehicles, the operative requirements placed on these assemblies have risen dramatically. Included among the main requirements are compressive strength, mechanical load-carrying capacity, and thermal and chemical resistance.
Brake lines are subjected to the following influences and loads:
- Mechanical stress: Steering and suspension movements on the vehicle
- Weather influences: Heat, cold, and ozone
- External influences: Water, grit, and oil
- Hydraulic pressure pulses: Pressures of up to 180 bar can briefly occur in hydraulic brake systems
As a result of these influences, brake hoses and brake lines need exceptional pulse strength, robust connecting elements, and high fatigue strength.
Legal regulations
The minimum requirements for marking, performance, mounting, and connections of brake hoses for vehicles are defined in the SAE J 1401, FMVSS 571.106, and ISO8 3996 norms.
Not only do the lines need to specify the manufacturer, but also the corresponding specification on the sleeve. A colored label or a label stamped or pressed into the material displaying axial rotation should also be present on the hose. A white longitudinal line extending across the length of the hose is typically provided. When a replacement is carried out, only brake hoses that correspond to this norm should therefore be used.
HELLA brake hoses surpass all SAEJ1401 specifications to ensure that we live up to our claim of providing the very highest levels of quality and safety.
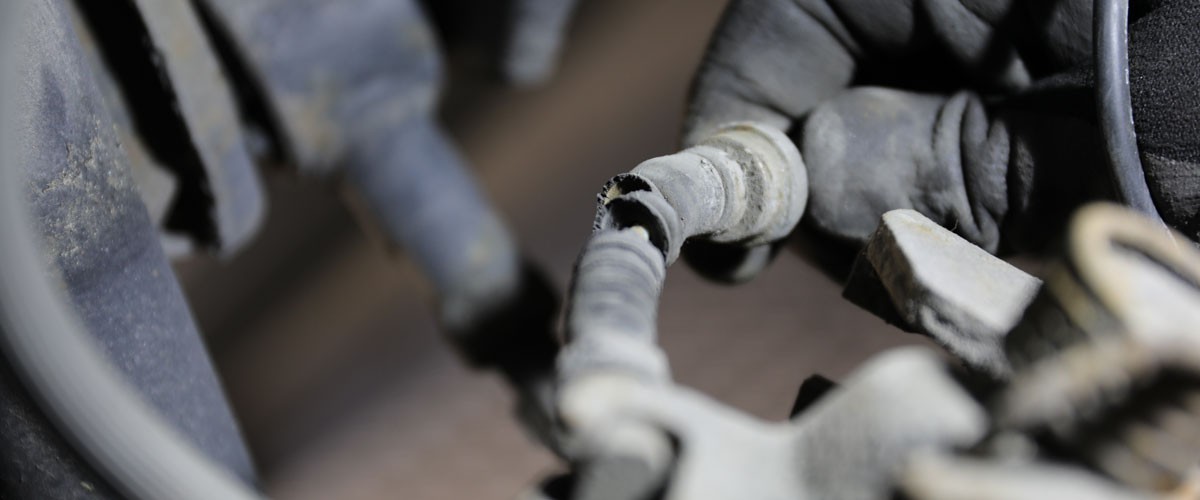
Brake line and brake hose faulty
Checking the brake line and brake hose
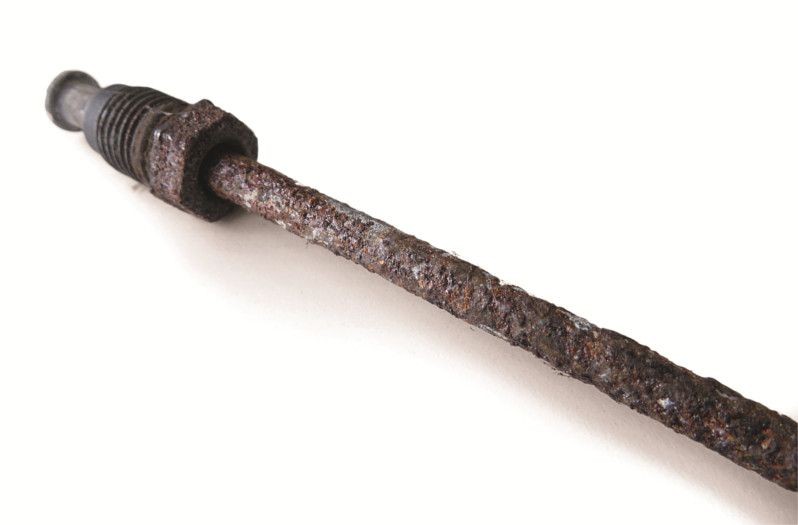
Brake lines and brake hoses are safety-relevant components and should be checked every time the vehicle is maintained. Typical defects include corrosion on the brake lines and damage to the hoses.
These defects can be caused by accidents, improper assembly, or aging. By carrying out a visual inspection, it is usually possible to detect chafing, cracks, bubble formation, corrosion, and other external damage with minimal outlay.
Assembly instructions
The following points should be taken into account by the technician when carrying out a repair:
- Mount brake hoses in a tension-free and contact-free manner
- Avoid twisting the hose and causing chafe marks
- Avoid contact with mineral oil and grease
- Ensure sufficient clearance for steering and suspension movements
- Avoid routing in the direct vicinity of exhaust systems
- Avoid excessively small bending radii (> 40 mm)
- Comply with the assembly information provided by the brake and vehicle manufacturers
Note!
Improper installation can negatively impact the driving characteristics of the vehicle and endanger lives.
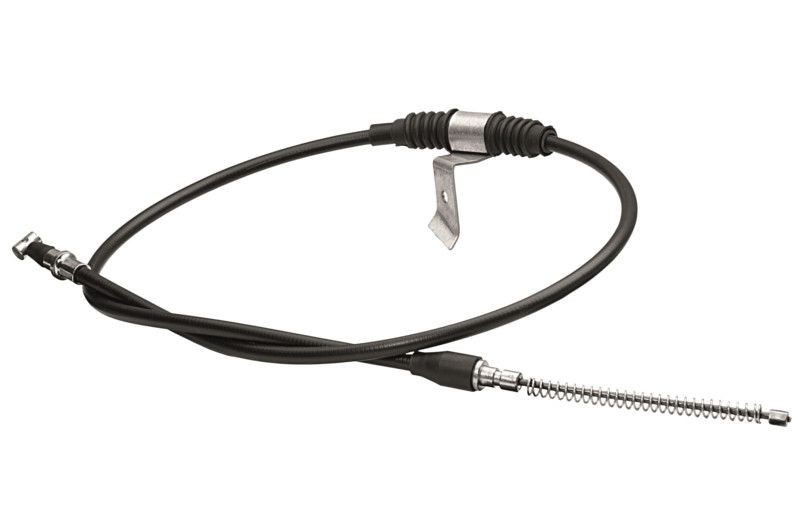
Handbrake cable
As required by law, multi-track vehicles must have two brake systems that operate independently from each other. A parking brake system is also required in addition to the service brake system. The parking brake, also called a hand-brake, is designed to prevent a vehicle that has come to a stop or has been parked from rolling away. When the mechanical hand-brake is actuated by pulling on the hand-brake lever, brake force is transferred via cables to the wheel brakes of the rear axle.
Hand-brake cables are subjected to the following influences or loads
- Mechanical stress caused by tensile force generated during actuation or movement in the axles or suspension of the vehicle
- Weather influences: Heat, cold, or ozone
- External influences: Water, grit, and oil
As a result of these influences, brake cables need exceptional tensile strength, robust sleeves, high-quality connecting elements, and high fatigue strength. A defective hand-brake cable is only noticeable when the parking brake fails.
The following defects can occur
- No or little braking effect
- Uneven braking effect
- Parking brake cannot be released
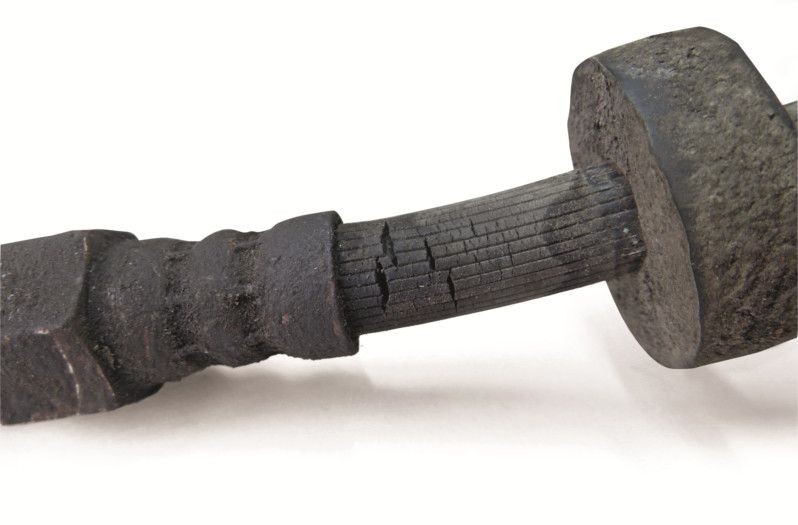
Handbrake cable faulty
- Undesired elongation of the hand-brake cables
- Changed elasticity as a result of overloading and hyperextension of the cable
- Compromised ease of motion
- Humidity and frost can cause the cables to seize, or freeze up
- Damaged sleeves or dust-protection collars can lead to direct exposure to water or dirt that can corrode and jam the cables
- Mechanical damage to sleeves or wire cables caused by incorrect assembly or overload
Checking the handbrake cable
Hand-brake cables can only be correctly adjusted if all components of the hand-brake system are fully functional. By carrying out a visual inspection, it is usually possible to detect chafing, cracks, corrosion, and other external damage with minimal outlay. Check exposed wire cables for breakage or splitting and replace if necessary. Check deflection rollers and guides for ease of movement and proper operation.
Notes on checking mechanically actuated hand-brakes
- The braking effect should be checked on a brake test stand
- No braking effect should be present when the first detent of the hand-brake lever is engaged
- The difference in the wheel circumference forces between the left and right wheels may not deviate by more than 30 percent from the highest value
- It must be possible to perform wheel lock braking with the parking brake
- If the actuation travel of the hand-brake lever is too long, the parking brake should be readjusted
Basic adjustment of the parking brake should be carried out when:
- The brake shoes of the drum brake are replaced
- A brake caliper with integrated hand-brake device is replaced
- Adjustment devices are replaced or reset
- The actuation travel is too long
- The hand-brake cables are replaced
The repair notes issued by the respective vehicle manufacturers must be observed in this context.
Assembly instructions
The following points should be taken into account by the technician when carrying out a repair:
- Mount brake cables in a tension-free and contact-free manner
- Avoid twisting and chafing
- Apply an appropriate amount of grease to connecting elements in areas where movement takes place
- Ensure sufficient clearance for steering and suspension movements
- Avoid routing in the direct vicinity of exhaust systems
- Comply with the assembly information provided by the brake and vehicle manufacturers!
How helpful is this article for you?
Success
Success
Success
Success
Error
Please tell us what you did not like.
Thank you for your feedback!
Wrong Captcha
Something went wrong
You might also be interested in