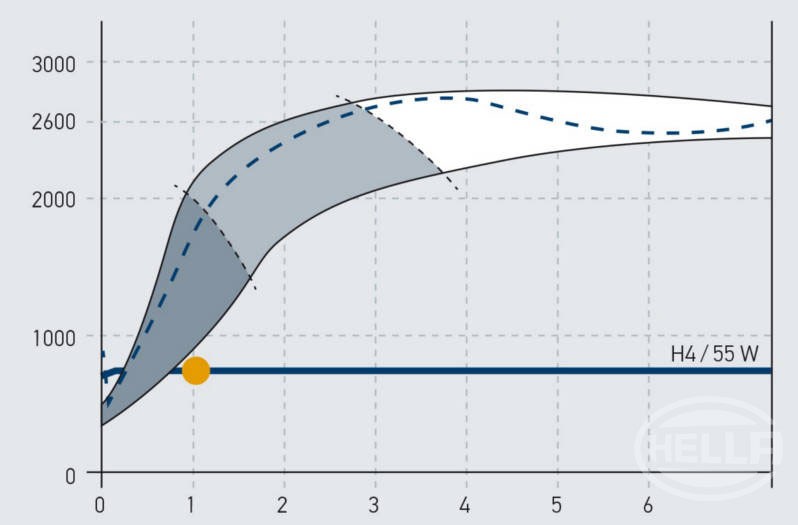
Xenon headlights
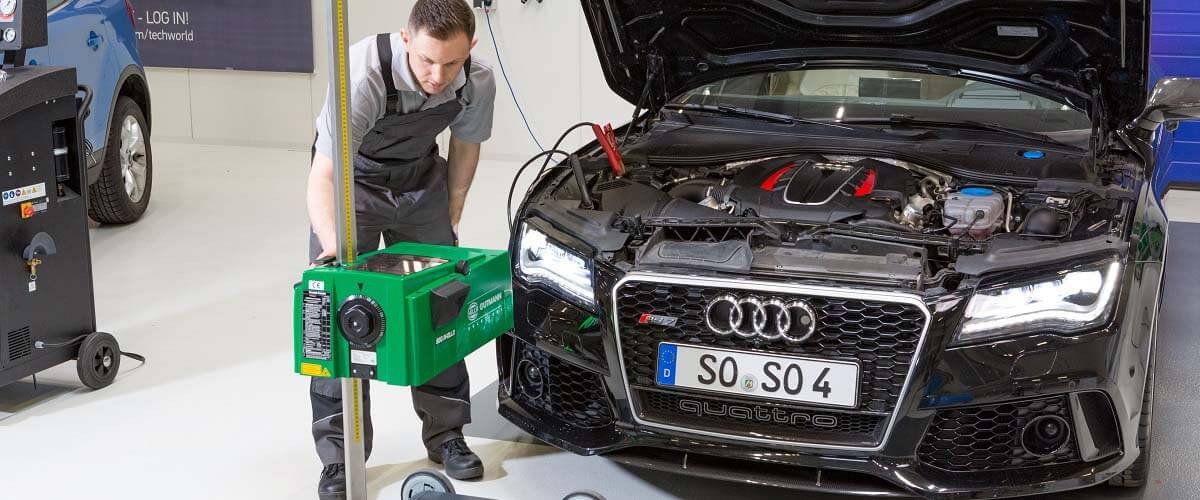
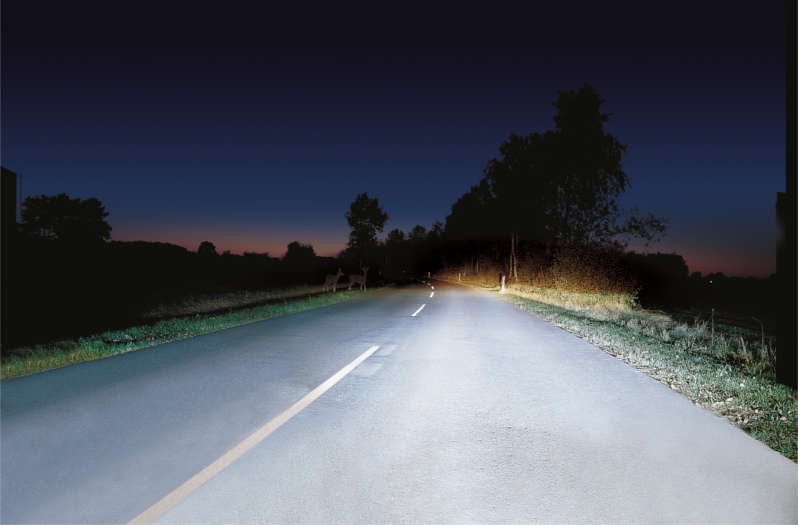
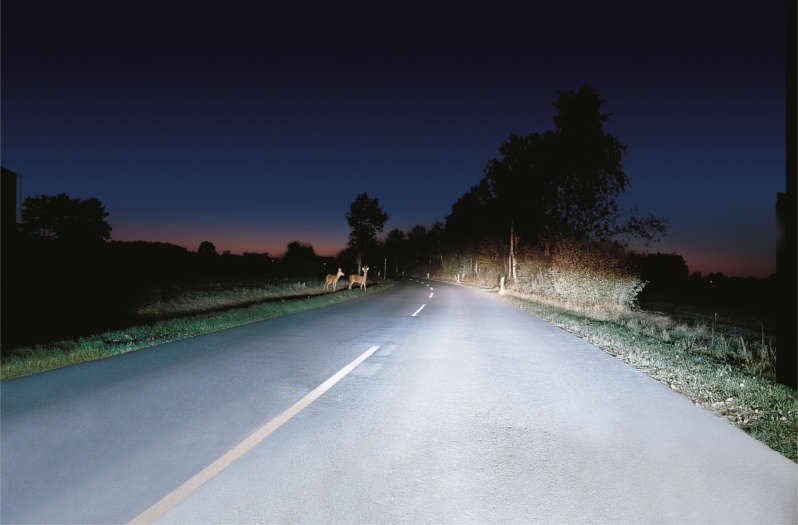
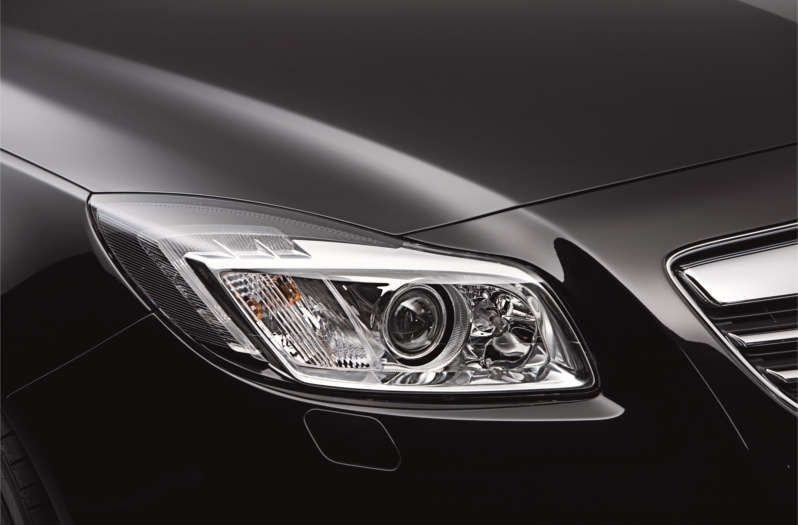
Xenon headlights provide substantially more light on the road than classic halogen headlamps. They increase safety when it is dark and are now found in almost all vehicle classes. On this page, find out about the structure of xenon headlights and how they work. You can also find out what causes xenon ballasts to fail, how faults can be found quickly, and how dangerous it is to retrofit illegal xenon headlights.
Important safety note
The following technical information and practical tips have been compiled by HELLA in order to provide professional support to vehicle workshops in their day-to-day work. The information provided on this website is intended for suitably qualified personnel only.
- 1. Function
- 2. Function
- 3. Cause of failure
- 4. Troubleshooting
- 5. Note
- 6. Useful information
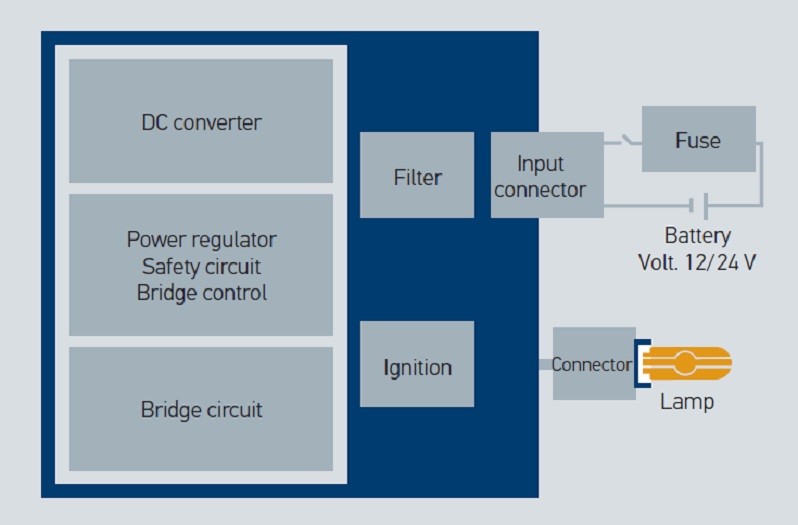
Bi-xenon headlights module
Xenon ballasts
Properties and differences of the 3rd / 4th generation compared to the 5th / 6th generation
| Features | 3rd generation | 4th generation | 5th generation | 6th generation (Xenius) |
| Burner | D2 | D2 | D1 | D1 / D3 |
| Internal igniter | X | |||
| External igniter | X | |||
| Filtered and shielded version | X | |||
| Fully shielded system | X | X | ||
| Longer cable possible | X | |||
| Improved ignition reliability | X | |||
| Laser-welded housing | X | X | ||
| All AFS functions integrated | X | |||
| LIN communication | X |
Faulty xenon ballast
A faulty ballast results in the complete failure of the headlamp.
Causes of failure of the ballast include:
- Lack of voltage supply
- Lack of ground connection
- Faulty electronics in the device
- Internal short circuits
Checking the xenon ballast
- Check whether the ballast attempts to ignite the bulb when the light is switched on. The ignition attempts can be clearly heard in the vicinity of the headlamp. If the ignition attempts are unsuccessful, the xenon bulb should be tested by using the bulb from the other headlamp.
- If no ignition attempt is carried out, the fuse should be checked.
- If the fuse is OK, check the voltage and ground supply directly on the ballast. Voltage must be at least 9 Volts.
- If the voltage and ground supply, as well as the xenon bulb, are OK, the cause of the fault is a faulty ballast.
Retrofitting xenon headlights – illegal retrofitting
Retrofitting xenon headlights – legal foundation
Technical background
- High glare values: Measurements in the lighting laboratory have shown that the active light distribution of a headlamp which was developed for halogen bulbs and is now operated illegally with a xenon light source no longer corresponds to the values calculated originally in any way.
- In the case of reflection systems, glare values were measured which exceed the permissible limit values by a factor of up to 100.
- The headlamps of these vehicles then no longer have a cut-off line and can also no longer be adjusted. The glare values correspond to those of high-beam headlamps. This endangers other road users massively.
How helpful is this article for you?
Success
Success
Success
Success
Error
Please tell us what you did not like.
Thank you for your feedback!
Wrong Captcha
Something went wrong
You might also be interested in