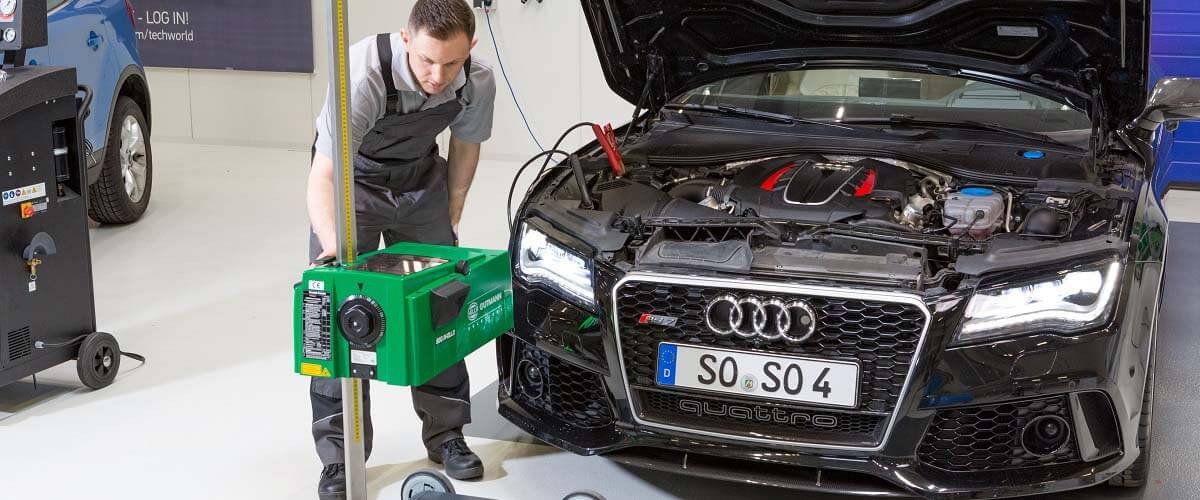
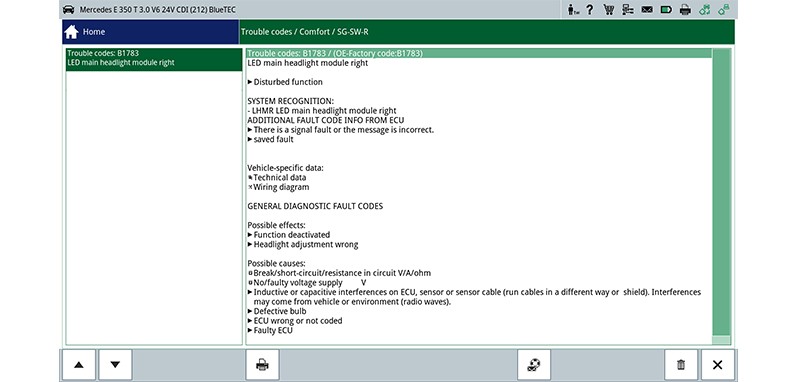
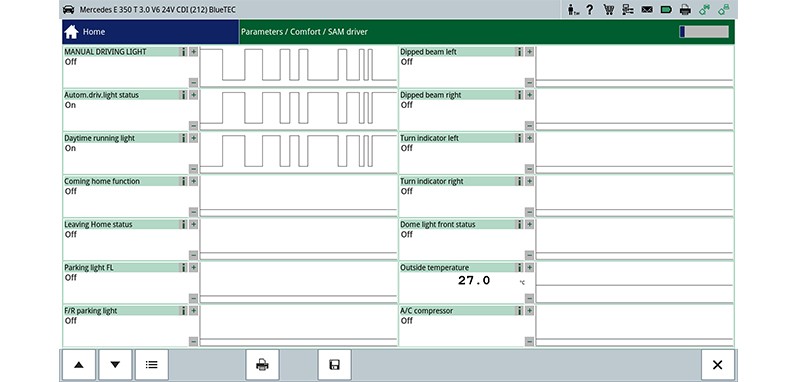
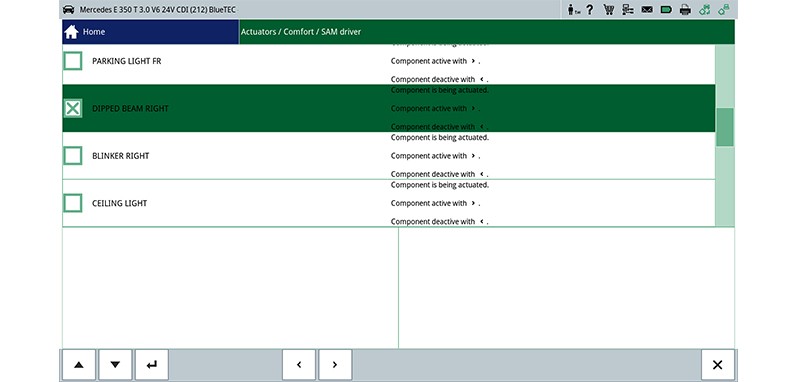
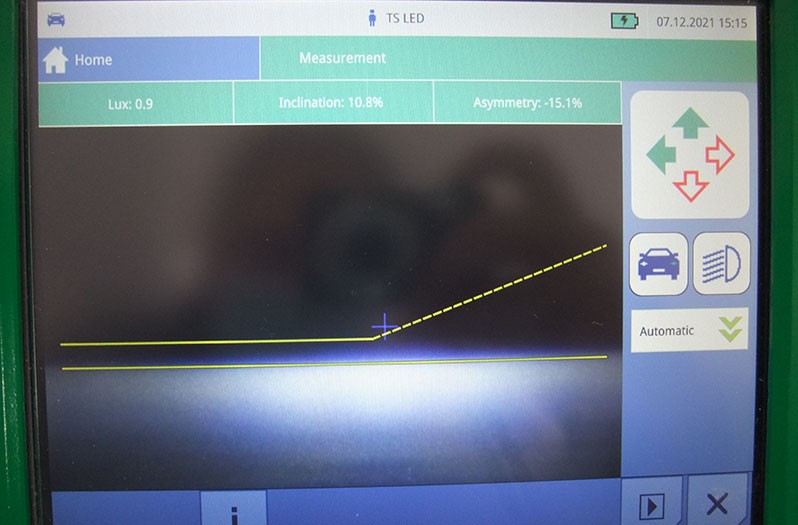
Carry out the following steps on the diagnostic device / vehicle
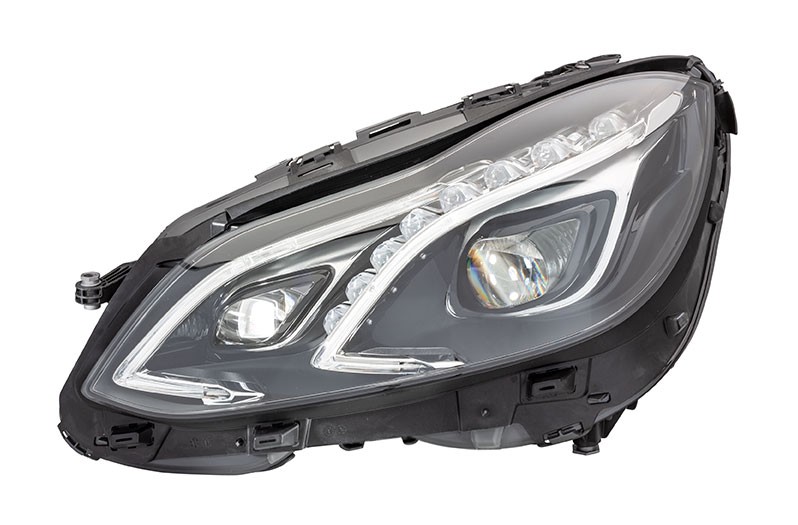
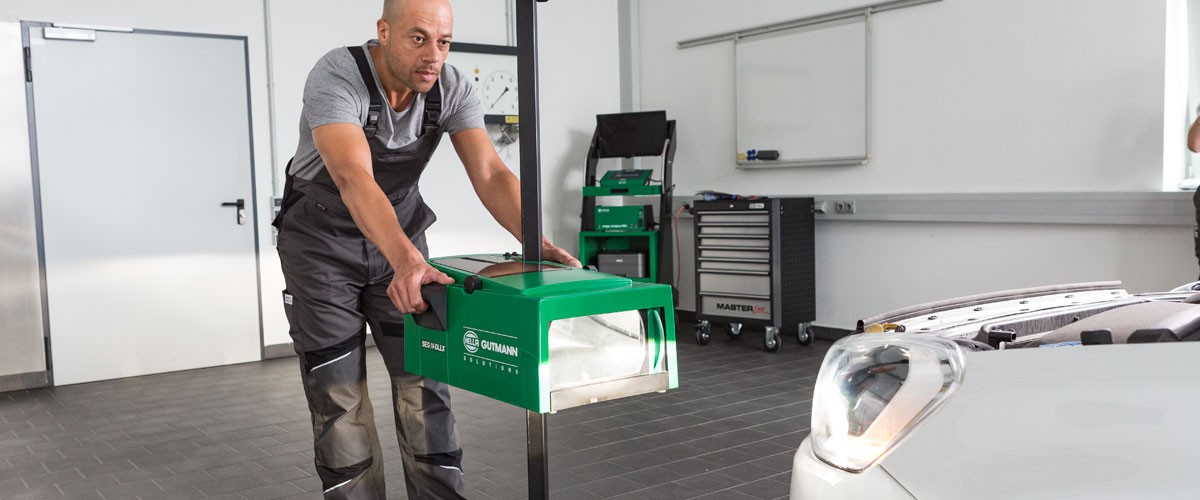
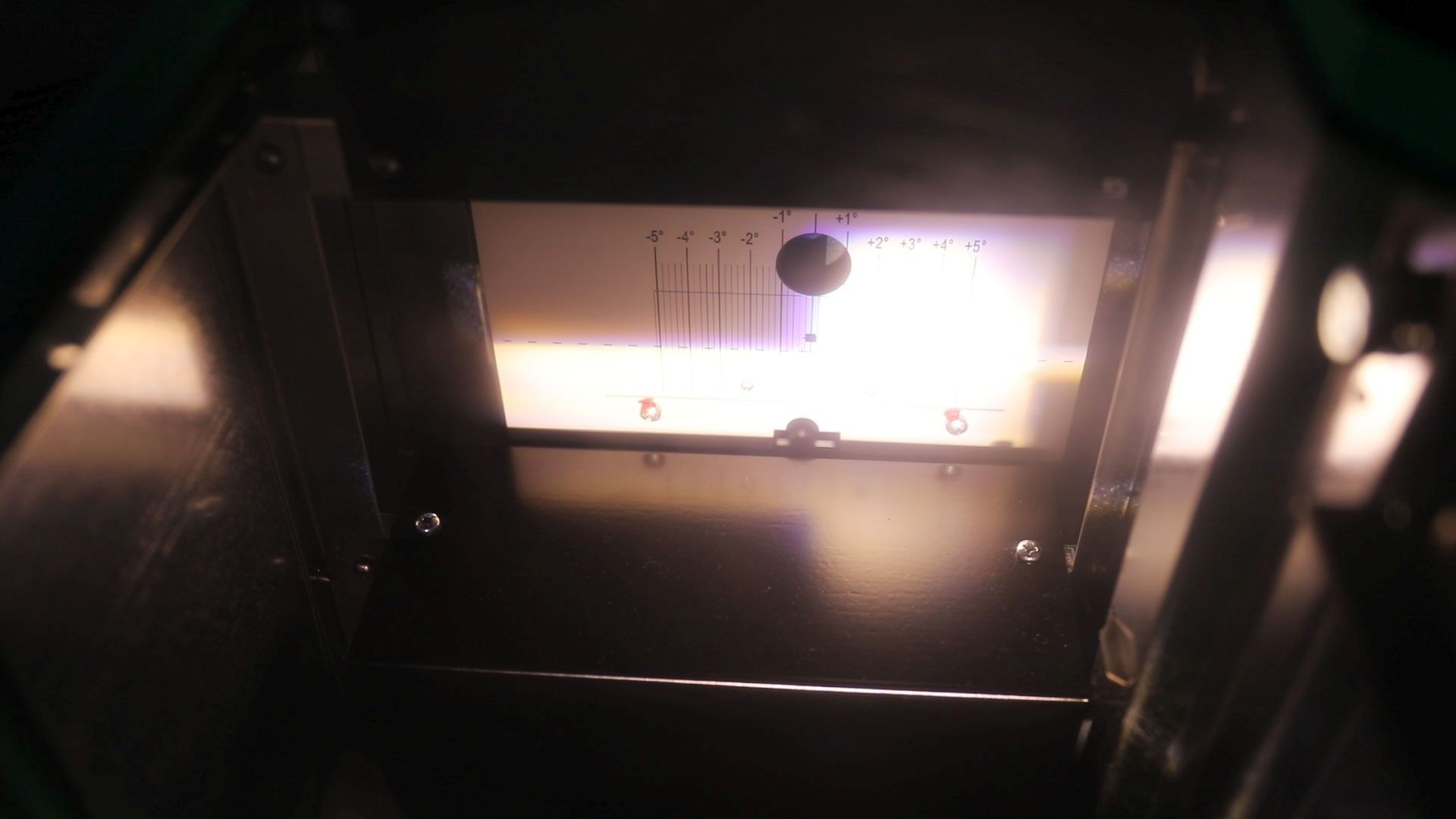
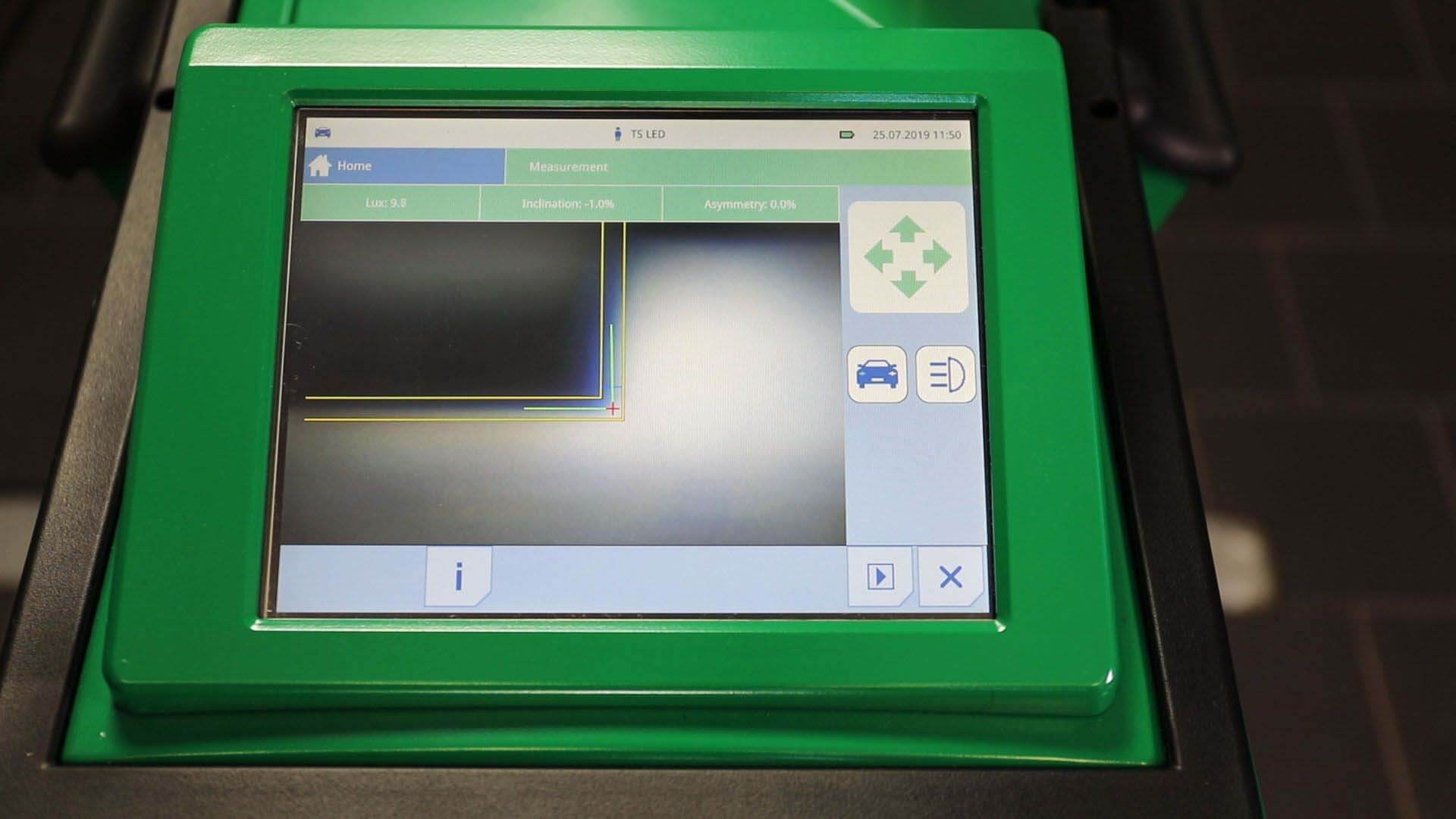
Connect a diagnostic device and then set up a beamsetter in front of the vehicle.
- Select vehicle
- Switch on the ignition
- Read out and clear error memory
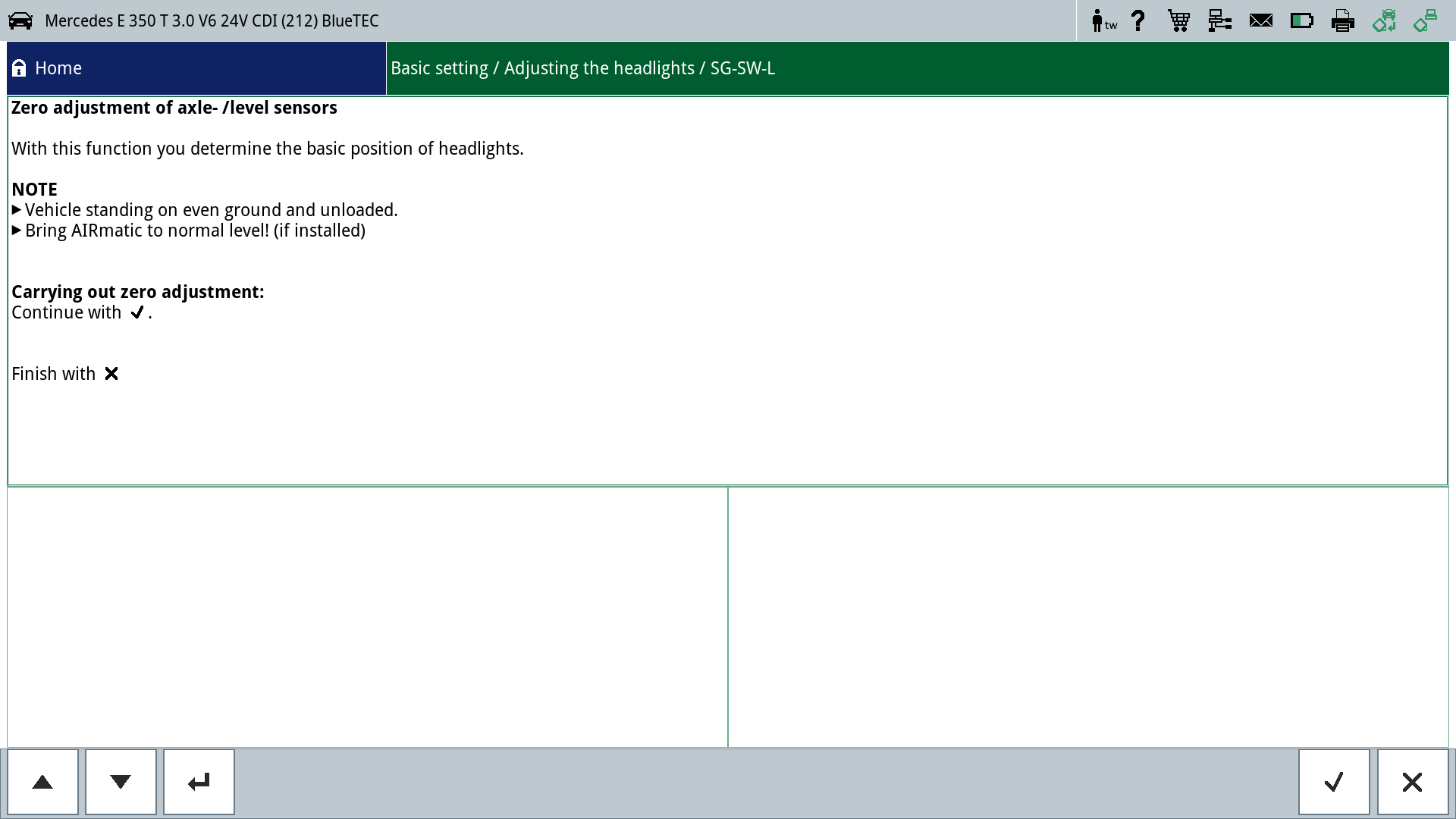
- Select basic setting "Adjust headlamp"
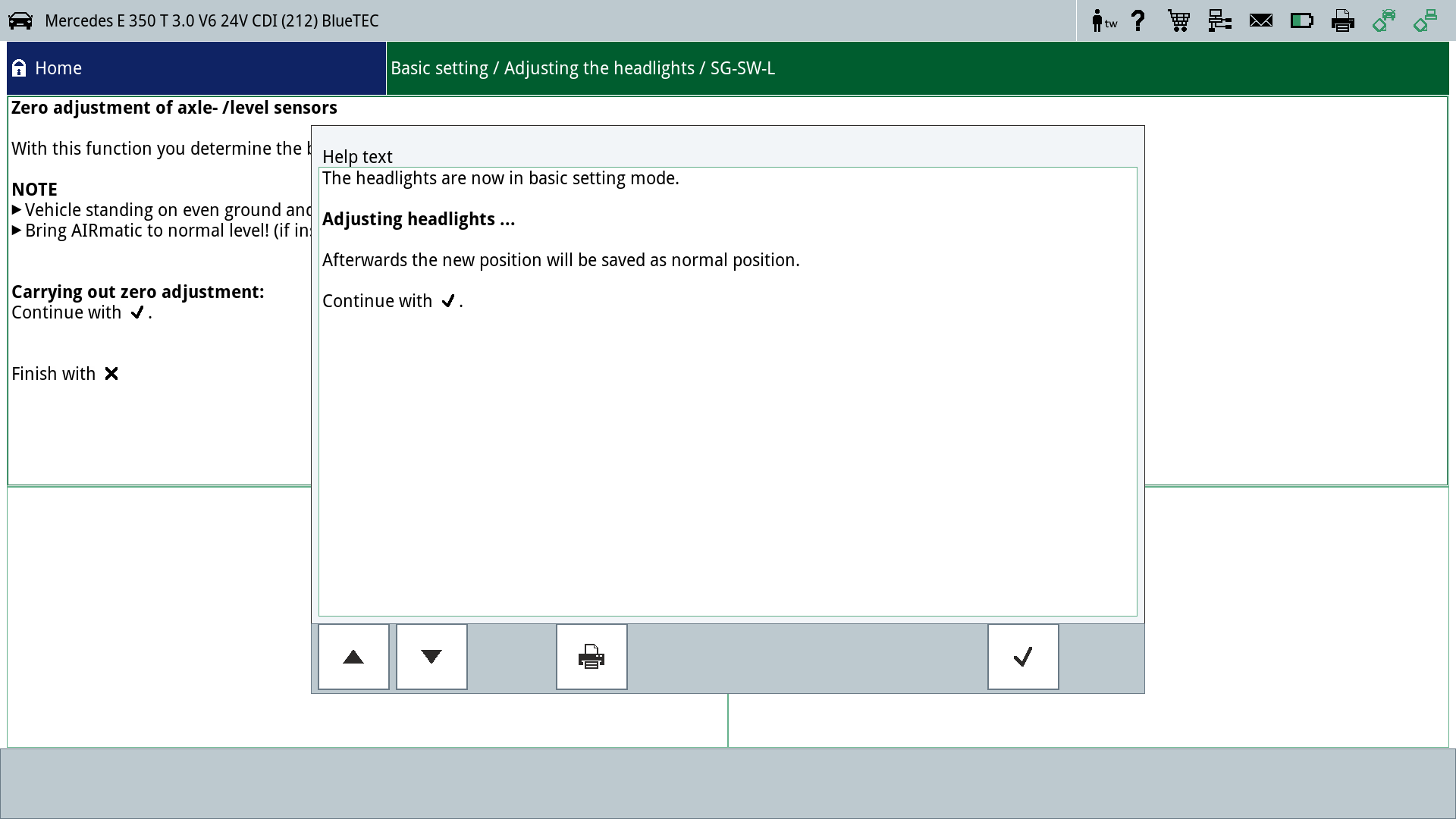
- Select zero setting
- Switch on headlamps
- Confirm zero setting. This sets the headlamps to the basic setting "Adjust headlamp".
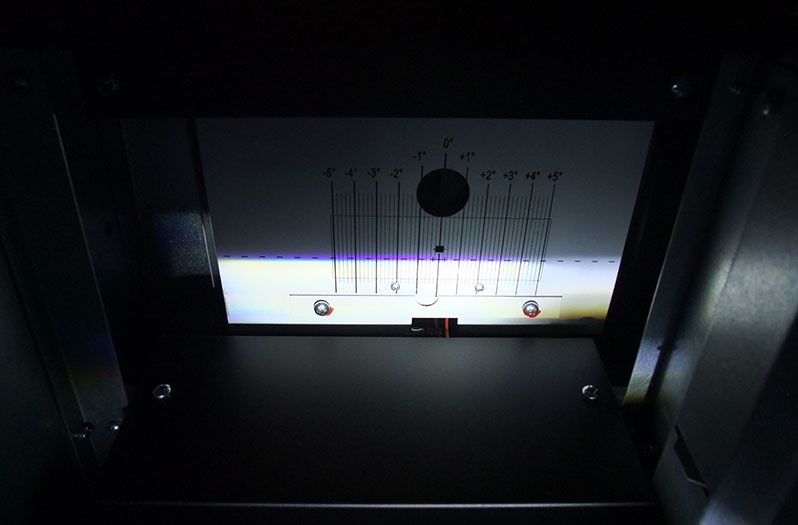
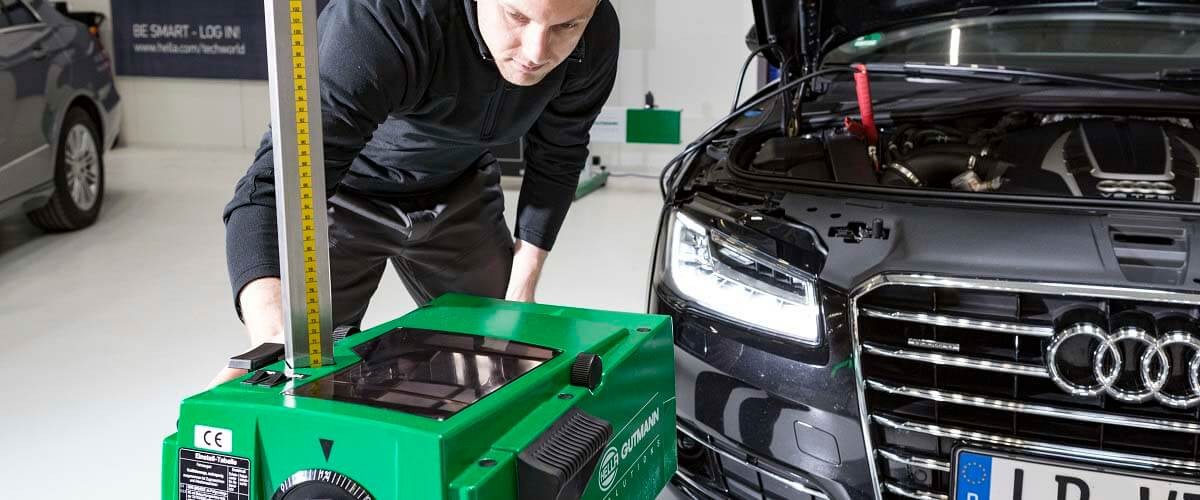
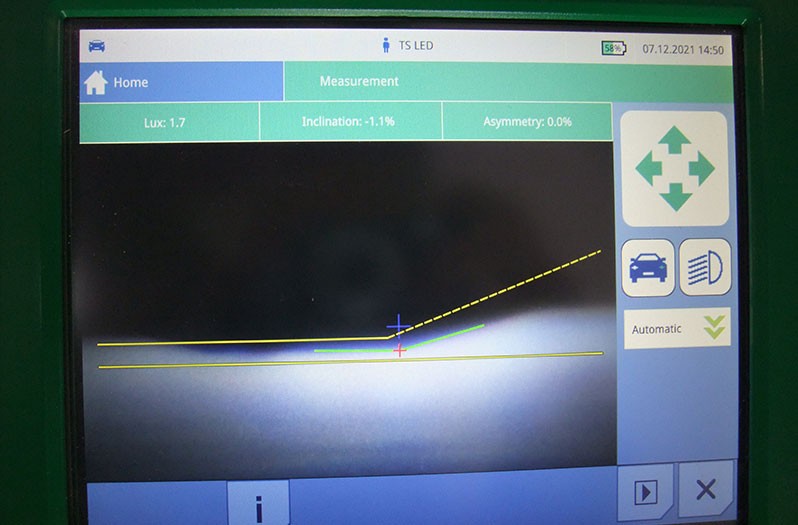
- Carry out headlamp adjustment, i.e. beam setting.