Great! Just one more Step
Subscription successful
Head to your inbox and confirm your email address so that you don’t miss our updates!
Get ready for brand new technical videos, car repair advice, trainings, helpful diagnostic tips, marketing campaigns and much more... delivered straight to your inbox every two weeks!
Stay Ahead of the Curve in the Automotive Industry!
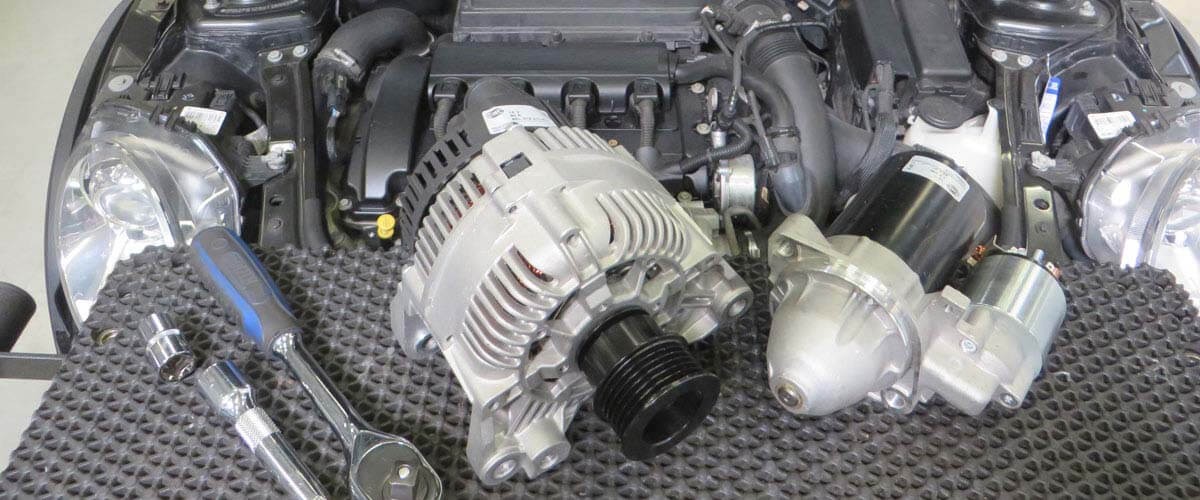
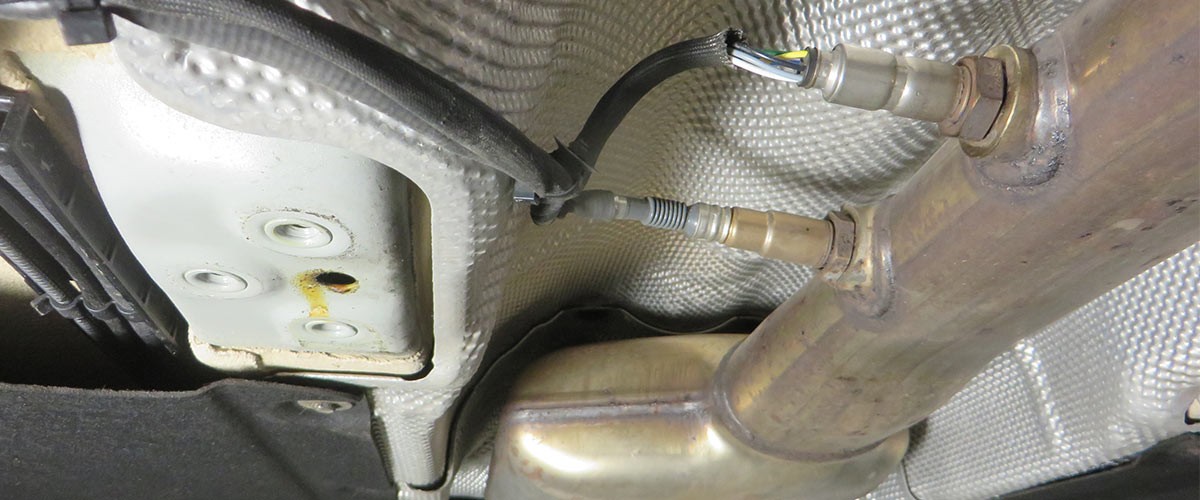
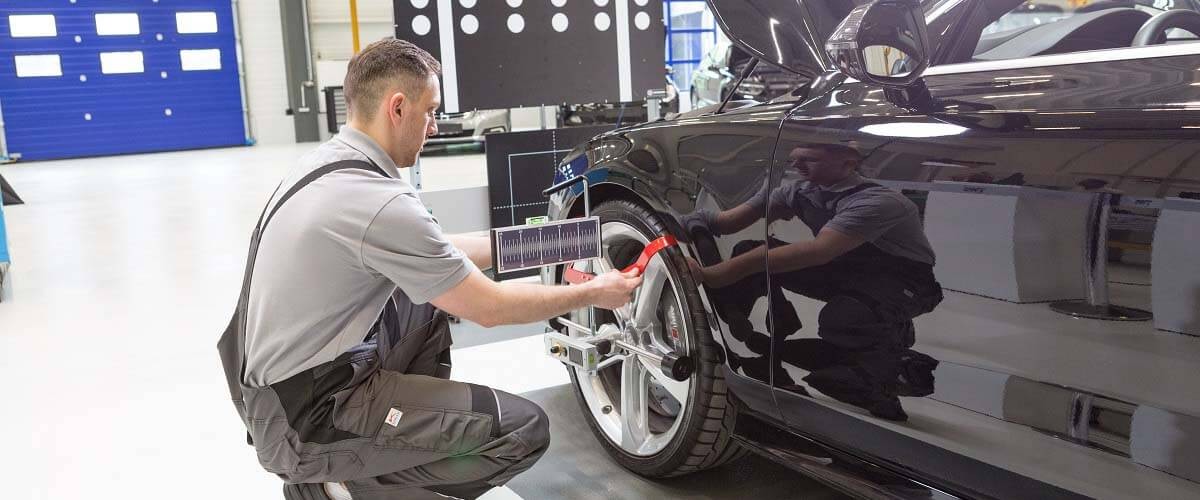
Sign up for our free HELLA TECH WORLD newsletter to receive the latest technical videos, car repair advice, training, marketing campaigns and diagnostic tips.
Together we can get cars back on the road quickly!
Success
Success
Success
Success
Error
Error
Please note: You will only be subscribed to the newsletter once you have clicked on the confirmation link in the notification e-mail you will receive shortly! Data Protection | Unsubscribe