Basic principles of car lighting technology
Lighting technology plays a very important role in motor vehicles with regard to the safety of vehicle occupants and that of other road users. On this page, we will explain to you the basic principles of automotive lighting technology and show you the design and function of the most common light sources. You will also find the causes for failure of light sources, as well as practical tips for their replacement.
Important safety note
The following technical information and practical tips have been compiled by HELLA in order to provide professional support to vehicle workshops in their day-to-day work. The information provided on this website is intended for suitably qualified personnel only.
- 1. Basic principles
- 2. Overview
- 3. Comparison
- 4. Practical tips
- 5. Parts identification
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
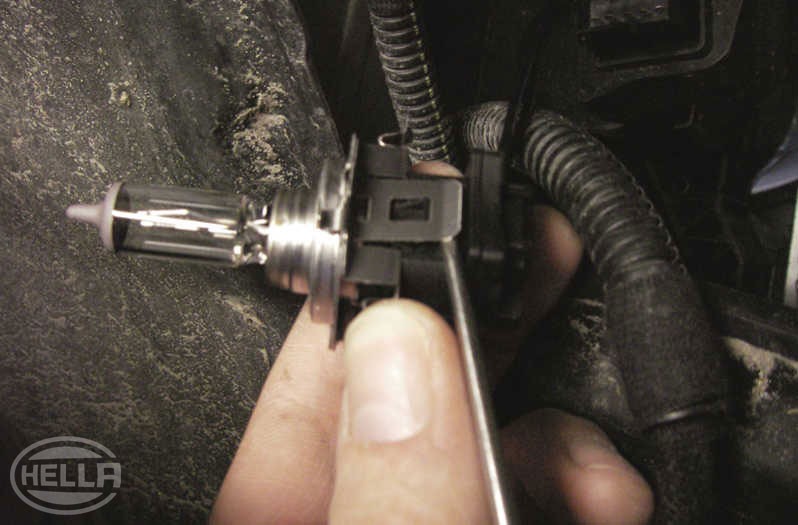
Despite regeneration within the bulb, the tungsten wire gradually becomes worn, thus limiting the service life.
Factors that influence a vehicle interior light source
- Filling pressure
- Filling gas
Positive factors of influence
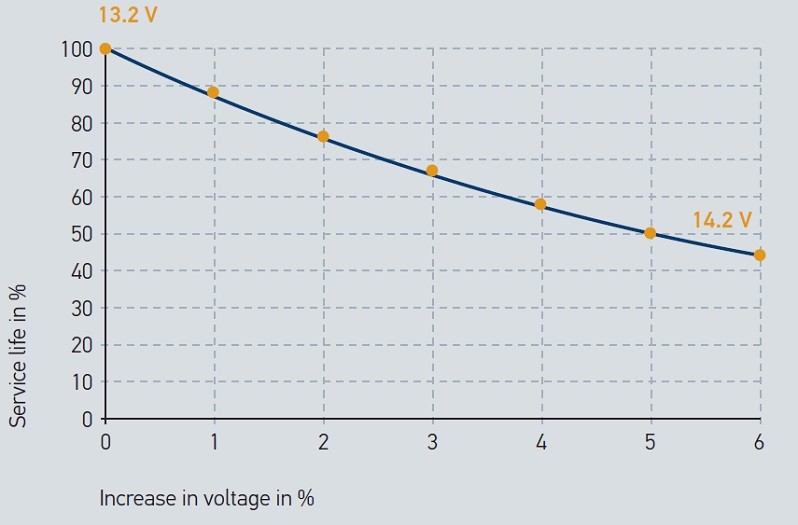
The service life and the luminous efficiency depend to a large extent on the existing supply voltage, among other factors.
As a rule of thumb it can be said: If the supply voltage of a light is increased by 5%, the luminous flux increases by 20% but at the same time the service life is cut by half.
Lighting technology tips - light sources
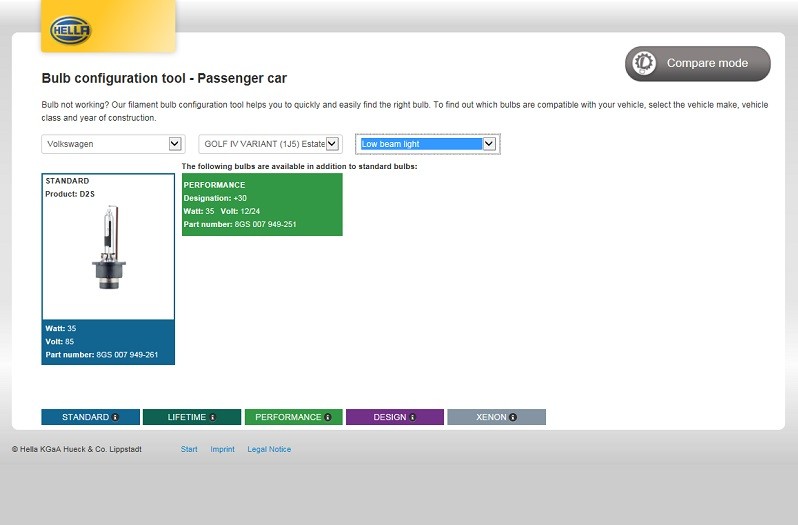
Bulb configuration tool - passenger cars
How helpful is this article for you?
Success
Success
Success
Success
Error
Please tell us what you did not like.
Thank you for your feedback!
Wrong Captcha
Something went wrong
You might also be interested in